Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Applications of genomic research in pediatric endocrine diseases
- Ja Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):520-530. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Recent advances in molecular genetics have improved our understanding of pediatric endocrine disorders and are now used in mainstream medical practice.
· Genome-wide association studies can increase our understanding of the biological mechanisms of disease and inform new therapeutic options.
· The identification of founder mutations leads to the efficient localization of the genes underlying Mendelian disorders.
· Next-generation sequencing technologies benefit clinical practice and research of pediatric endocrinology.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Ozlem Kara, Hanife Aysegul Arsoy, Murat Keskin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):395-402. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: Is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adolescents?
Finding: The frequency of NAFLD did not increase in adolescents with PCOS. However, hyperandrogenemia was a risk factor for NAFLD.
Meaning: Adolescents with PCOS and hyperandrogenemia should be closely monitored for hepatic steatosis.
- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Spontaneous movements as prognostic tool of neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: a narrative review
- Hyun Iee Shin, Myung Woo Park, Woo Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):458-464. Published online May 16, 2023
-
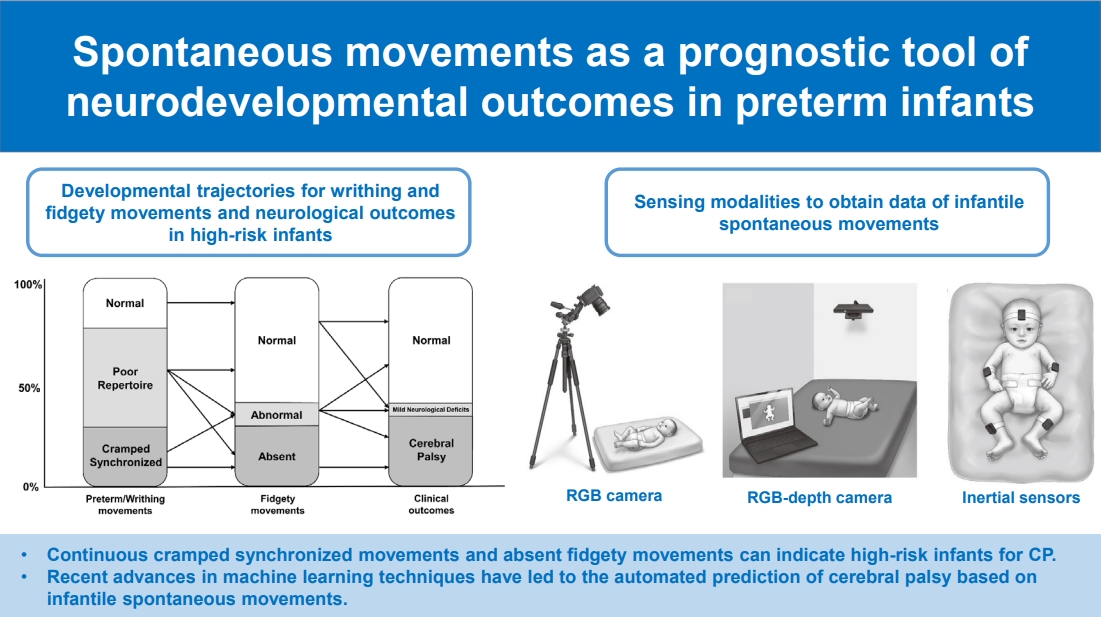
· Spontaneous movements can be useful to evaluate neuronal integrity in preterm infants.
· In General Movements Assessment, continuous cramped synchronized movements and absent fidgety movements can indicate high-risk infants for cerebral palsy.
· Recent advances in machine learning techniques have led to the automated prediction of cerebral palsy based on infantile spontaneous movements.
- Infection
- Pathogenetic and etiologic considerations of febrile seizures
- Ji Yoon Han, Seung Beom Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):46-53. Published online January 13, 2023
-
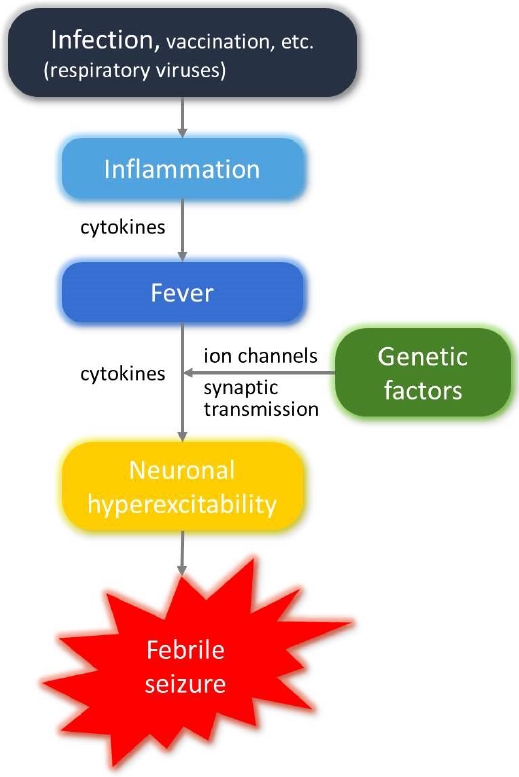
· Inflammatory responses accompanying fever increase neuronal excitability in the central nervous system, which in turn provokes seizures.
· Fever in children with febrile seizures is usually caused by common respiratory viruses, the distributions of which match those of seasonal community-acquired respiratory tract infections.
· Several genetic variations in ion channels seem associated with neuronal hyperexcitability in children with febrile seizures.
- Gastroenterology
- Update on eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease beyond eosinophilic esophagitis in children
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):233-239. Published online January 3, 2023
-
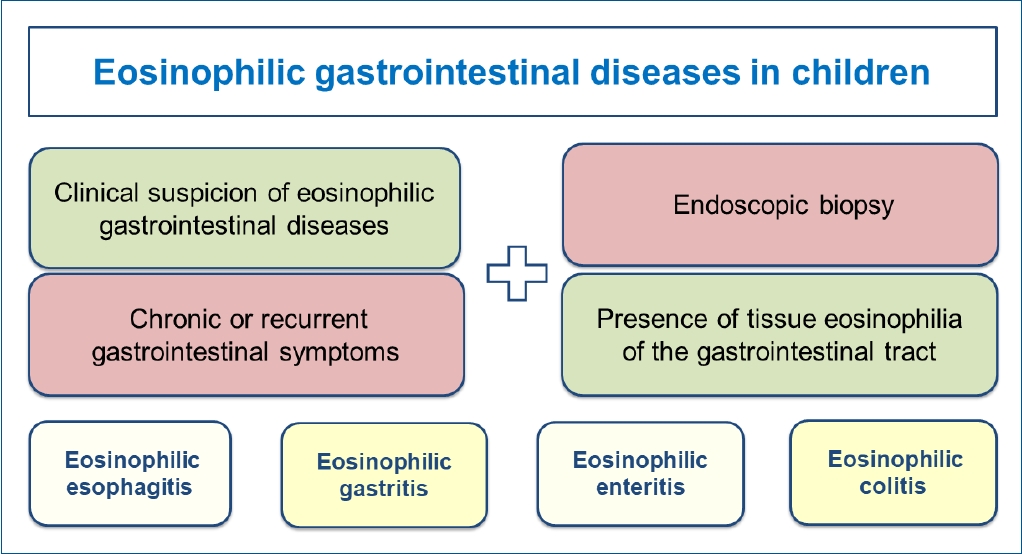
· Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease (EGID) is uncommon, with a prevalence of 1–30/100,000 in the general population; however, it is increasing worldwide.
· The diagnosis of EGID is based on histopathological findings of endoscopic mucosal biopsy in which tissue eosinophils are counted in each gastrointestinal tract segment of patients with chronic or recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms.
· Individualized treatment strategies, including adequate dietary and pharmacological therapy, may help improve outcomes of children with EGID.
- Endocrinology
- Genetic factors in precocious puberty
- Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):172-181. Published online October 18, 2021
-
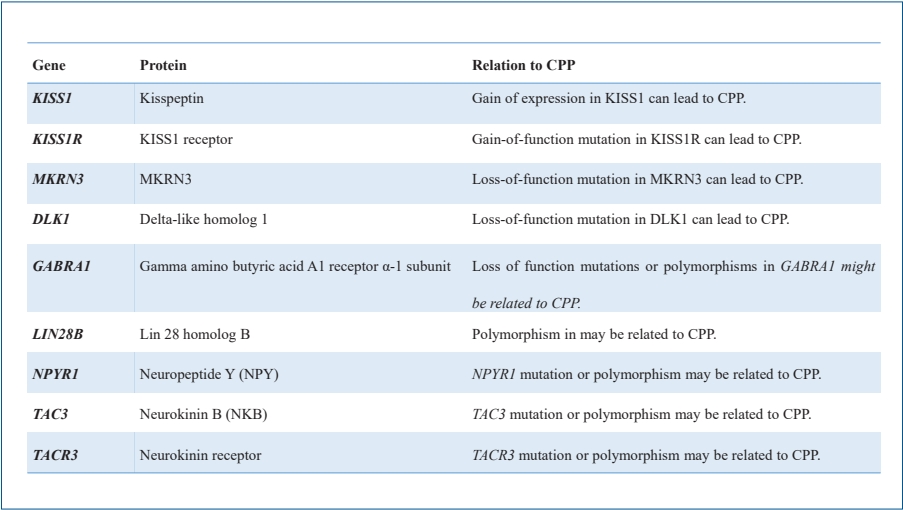
· Mutations in the kisspeptin (KISS1), kisspeptin receptor (KISS1R), makorin ring finger protein 3 (MKRN3), and delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) genes are associated with idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP).
· A few genes related to pubertal onset have been implicated in ICPP.
· Epigenetic factors such as DNA methylation, histone posttranslational modifications, and noncoding ribonucleic acids may be related to ICPP
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Obesity and chronic kidney disease: prevalence, mechanism, and management
- Hyung Eun Yim, Kee Hwan Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):511-518. Published online April 6, 2021
-

· Obesity is strongly associated with the development and progression of chronic kidney disease.
· Altered renal hemodynamics, metabolic effects, and lipid nephrotoxicity may play a key role in the development of obesity-related kidney disease.
· Children born to obese mothers are at increased risk of developing obesity and chronic kidney disease later in life.
· A multilevel approach is needed to prevent obesity and related chronic diseases.
- Immunology
- Modern diagnostic capabilities of neonatal screening for primary immunodeficiencies in newborns
- Evgenia Olegovna Khalturina, Natalia Dmitrievna Degtyareva, Anastasiia Vasi’evna Bairashevskaia, Alena Valerievna Mulenkova, Anna Vladimirovna Degtyareva
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):504-510. Published online March 25, 2021
-
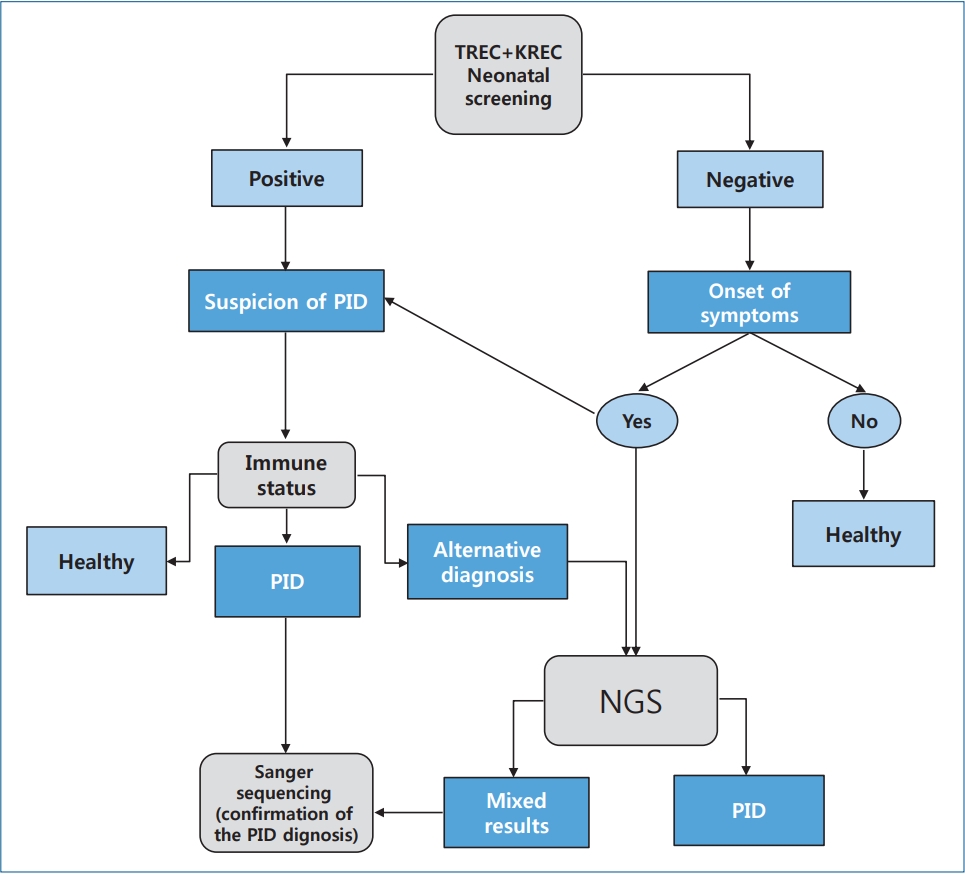
· Neonatal screening for primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDs) enables early diagnosis and subsequent initiation of therapy.
· Excision of T-cell receptors and kappa-recombination excision circles are cheaper alternative PID screening methods.
· Sanger DNA sequencing remains the reference method for detecting PID; however, next-generation sequencing technology is increasingly used to diagnose it.
· Here we developed a graphical algorithm for diagnosing primary immunodeficiency syndrome based on modern methods of screening for primary immunodeficiencies in newborns.
- Allergy
- Eosinophils and childhood asthma
- Bong Seok Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):60-67. Published online January 6, 2021
-
•In allergic eosinophilic asthma, eosinophils act as important effector cells and antigen-presenting cells, while in nonallergic eosinophilic asthma, type 2 innate lymphoid cells play an important role in eosinophil activation.
•Sputum eosinophil counts can be helpful for evaluating allergic airway inflammation in asthma.
• Anti-interleukin-5 has broadened the scope of asthma treatment.
- Immunology
- Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 and early immunomodulators
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):239-250. Published online June 18, 2020
-
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading globally. Although its etiologic agent is discovered as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there are many unsolved issues in COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. The causes of different clinical phenotypes and incubation periods among individuals, species specificity, and cytokine storm with lymphopenia as well as the mechanism of damage to organ...
- Neurology
- Genetic tests by next-generation sequencing in children with developmental delay and/or intellectual disability
- Ji Yoon Han, In Goo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):195-202. Published online November 4, 2019
-
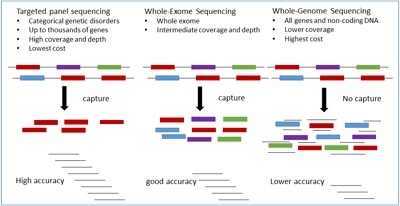
Developments in next-generation sequencing (NGS) techogies have assisted in clarifying the diagnosis and treatment of developmental delay/intellectual disability (DD/ID) via molecular genetic testing. Advances in DNA sequencing technology have not only allowed the evolution of targeted panels but also, and more currently enabled genome-wide analyses to progress from research era to clinical practice. Broad acceptance of accuracy- guided targeted gene...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Changes of Bax, Bcl-2, CCR-2, MCP-1, and TGF-β1 genes in the left ventricle of spontaneously hypertensive rat after losartan treatment
- Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):95-101. Published online October 24, 2018
-
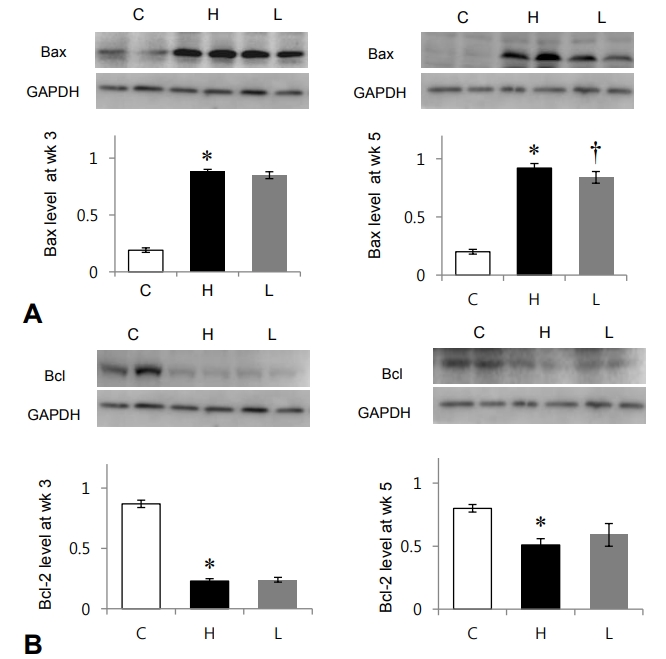
Purpose: Increased apoptosis was recently found in the hypertrophied left ventricle of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). Although the available evidence suggests that apoptosis can be induced in cardiac cells by various insults including pressure overload, cardiac apoptosis appears to result from an exaggerated local production of angiotensin in adult SHRs. Altered expressions of Bcl associated X (Bax), Bcl-2, chemokine receptor...
- Case Report
- Genetics and Metabolism
- The first Korean case with Floating-Harbor syndrome with a novel SRCAP mutation diagnosed by targeted exome sequencing
- Eun Mi Choi, Dong Hyun Lee, Seok Jin Kang, Ye Jee Shim, Heung Sik Kim, Jun Sik Kim, Jong In Jeong, Jung-Sook Ha, Ja-Hyun Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):403-406. Published online September 16, 2018
-
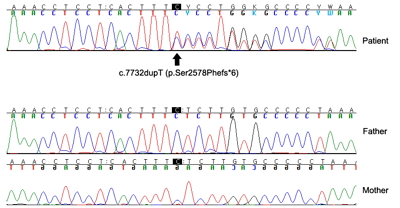
Floating-Harbor syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder associated with SRCAP mutation. To date, approximately 50 cases of Floating-Harbor syndrome have been reported, but none have been reported in Korea yet. Floating-Harbor syndrome is characterized by delayed bony maturation, unique facial features, and language impairment. Here, we present a 6-year-old boy with a triangular face, deep-set protruding eyes, low-set...
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Epilepsy syndromes during the first year of life and the usefulness of an epilepsy gene panel
- Eun Hye Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(4):101-107. Published online April 23, 2018
-
Recent advances in genetics have determined that a number of epilepsy syndromes that occur in the first year of life are associated with genetic etiologies. These syndromes range from benign familial epilepsy syndromes to early-onset epileptic encephalopathies that lead to poor prognoses and severe psychomotor retardation. An early genetic diagnosis can save time and overall cost by reducing the amount...
- Original Article
- Oncology
- Excellent treatment outcomes in children younger than 18 months with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma - Chiwoo Kim, Young Bae Choi, Ji Won Lee, Keon Hee Yoo, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):53-58. Published online February 28, 2018
-

Purpose Although the prognosis is generally good in patients with intermediate-risk neuroblastoma, no consensus has been reached on the ideal treatment regimen. This study analyzed treatment outcomes and toxicities in patients younger than 18 months with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma.Methods We retrospectively analyzed 20 patients younger than 18 months newly diagnosed with stage 4
MYCN nonamplified neuroblastoma between January 2009 and...
- Endocrinology
- Screening of
SHOX gene sequence variants in Saudi Arabian children with idiopathic short stature - Abdulla A. Alharthi, Ehab I. El-Hallous, Iman M. Talaat, Hamed A. Alghamdi, Matar I. Almalki, Ahmed Gaber
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(10):327-332. Published online October 20, 2017
-
Purpose Short stature affects approximately 2%–3% of children, representing one of the most frequent disorders for which clinical attention is sought during childhood. Despite assumed genetic heterogeneity, mutations or deletions in the short stature homeobox-containing gene (
SHOX ) are frequently detected in subjects with short stature. Idiopathic short stature (ISS) refers to patients with short stature for various unknown reasons. The goal...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Genetics of hereditary nephrotic syndrome: a clinical review
- Tae-Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):55-63. Published online March 27, 2017
-

Advances in podocytology and genetic techniques have expanded our understanding of the pathogenesis of hereditary steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). In the past 20 years, over 45 genetic mutations have been identified in patients with hereditary SRNS. Genetic mutations on structural and functional molecules in podocytes can lead to serious injury in the podocytes themselves and in adjacent structures, causing sclerotic...
- Neurology
- Malformations of cortical development: genetic mechanisms and diagnostic approach
- Jeehun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(1):1-9. Published online January 31, 2017
-
Malformations of cortical development are rare congenital anomalies of the cerebral cortex, wherein patients present with intractable epilepsy and various degrees of developmental delay. Cases show a spectrum of anomalous cortical formations with diverse anatomic and morphological abnormalities, a variety of genetic causes, and different clinical presentations. Brain magnetic resonance imaging has been of great help in determining the exact...
- Case Report
- Genetics and Metabolism
- A nonsense
PAX6 mutation in a family with congenital aniridia - Kyoung Hee Han, Hye Jin Lee, Il-Soo Ha, Hee Gyung Kang, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S1-S4. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Congenital aniridia is a rare ocular malformation that presents with severe hypoplasia of the iris and various ocular manifestations. Most cases of congenital aniridia are known to be related to mutations in the paired box gene-6 (
PAX6 ), which is an essential gene in eye development. Herein, we report a familial case of autosomal dominant congenital aniridia with four affected members...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- The effect of sildenafil on right ventricular remodeling in a rat model of monocrotaline-induced right ventricular failure
- Hyun Kyung Bae, Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(6):262-270. Published online June 30, 2016
-
Purpose Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) leads to right ventricular failure (RVF) as well as an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance. Our purpose was to study the effect of sildenafil on right ventricular remodeling in a rat model of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced RVF.
Methods The rats were distributed randomly into 3 groups. The control (C) group, the monocrotaline (M) group (MCT 60 mg/kg) and the...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: an immunological concept
- Seong Heon Kim, Se Jin Park, Kyoung Hee Han, Andreas Kronbichler, Moin A. Saleem, Jun Oh, Beom Jin Lim, Jae Il Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(5):205-211. Published online May 31, 2016
-
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in children is characterized by massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) is the most common form of INS in children. The pathogenesis of MCNS still remains unclear, however, several hypotheses have been recently proposed. For several decades, MCNS has been considered a T-cell disorder, which causes the impairment of the glomerular filtration barrier...
- Case Report
- Oncology
- Early onset of colorectal cancer in a 13-year-old girl with Lynch syndrome
- Do Hee Ahn, Jung Hee Rho, Hann Tchah, In-Sang Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(1):40-42. Published online January 22, 2016
-
Lynch syndrome is the most common inherited colon cancer syndrome. Patients with Lynch syndrome develop a range of cancers including colorectal cancer (CRC) and carry a mutation on one of the mismatched repair (MMR) genes. Although CRC usually occurs after the fourth decade in patients with Lynch syndrome harboring a heterozygous MMR gene mutation, it can occur in children with...
- Review Article
- Early-onset epileptic encephalopathies and the diagnostic approach to underlying causes
- Su-Kyeong Hwang, Soonhak Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):407-414. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Early-onset epileptic encephalopathies are one of the most severe early onset epilepsies that can lead to progressive psychomotor impairment. These syndromes result from identifiable primary causes, such as structural, neurodegenerative, metabolic, or genetic defects, and an increasing number of novel genetic causes continue to be uncovered. A typical diagnostic approach includes documentation of anamnesis, determination of seizure semiology, electroencephalography, and...
- Update of genetic susceptibility in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Kyung Lim Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(3):84-88. Published online March 20, 2015
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis that predominantly affects children, and can result in coronary artery lesions (CAL). A patient with KD who is resistant to treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) has a higher risk of developing CAL. Incomplete KD has increased in prevalence in recent years, and is another risk factor for the development of CAL. Although...
- Recent update of autism spectrum disorders
- Sung Koo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(1):8-14. Published online January 31, 2015
-
In patients with a language developmental delay, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis for autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), specific language impairment, and mental retardation. It is important that pediatricians recognize the signs and symptoms of ASDs, as many patients with language developmental delays are ultimately diagnosed with ASDs. Pediatricians play an important role in the early recognition of...
- Case Report
- Necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome secondary to varicella in a healthy child
- Byung Ok Kwak, Min Jung Lee, Hye Won Park, Min Kyung Song, Sochung Chung, Kyo Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):538-541. Published online December 31, 2014
-
Varicella is usually considered to be a benign disease in healthy children; however, serious complications can occur such as necrotizing fasciitis and toxic shock syndrome. We describe a 38-month-old girl with necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome following varicella. She was previously healthy and vaccinated against varicella at 12 months of age. She had been diagnosed with varicella three...
- A Korean boy with atypical X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy confirmed by an unpublished mutation of
ABCD1 - Hye Jeong Jwa, Keon Su Lee, Gu Hwan Kim, Han Wook Yoo, Han Hyuk Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(9):416-419. Published online September 30, 2014
-
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a rare peroxisomal disorder, that is rapidly progressive, neurodegenerative, and recessive, and characteristically primary affects the central nervous system white matter and the adrenal cortex. X-ALD is diagnosed basaed on clinical, radiological, and serological parameters, including elevated plasma levels of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), such as C24:0 and C26:0, and high C24:0/C22:0 and C26:0/C22:0...
- Original Article
- Neurofibromatosis type 1: a single center's experience in Korea
- Min Jeong Kim, Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(9):410-415. Published online September 30, 2014
-
Purpose Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant condition caused by an
NF1 gene mutation. NF1 is also a multisystem disorder that primarily affects the skin and nervous system. The goal of this study was to delineate the phenotypic characterization and assess theNF1 mutational spectrum in patients with NF1.Methods A total of 42 patients, 14 females and 28 males, were enrolled...
- Case Report
- Identification of a novel mutation in a patient with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia
- Ye Seung Lee, Hui Kwon Kim, Hye Rim Kim, Jong Yoon Lee, Joong Wan Choi, Eun Ju Bae, Phil Soo Oh, Won Il Park, Chang Seok Ki, Hong Jin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(5):240-244. Published online May 31, 2014
-
Pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia (PHP Ia) is a disorder characterized by multiform hormonal resistance including parathyroid hormone (PTH) resistance and Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO). It is caused by heterozygous inactivating mutations within the Gs alpha-encoding GNAS exons. A 9-year-old boy presented with clinical and laboratory abnormalities including hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, PTH resistance, multihormone resistance and AHO (round face, short stature, obesity, brachydactyly...
- Review Article
- Genetic risk factors associated with respiratory distress syndrome
- Heui Seung Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):157-163. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) among preterm infants is typically due to a quantitative deficiency of pulmonary surfactant. Aside from the degree of prematurity, diverse environmental and genetic factors can affect the development of RDS. The variance of the risk of RDS in various races/ethnicities or monozygotic/dizygotic twins has suggested genetic influences on this disorder. So far, several specific mutations in...
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







