Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Cognitive outcomes in late childhood and adolescence of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Bo Lyun Lee, Hannah C. Glass
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):608-618. Published online May 24, 2021
-
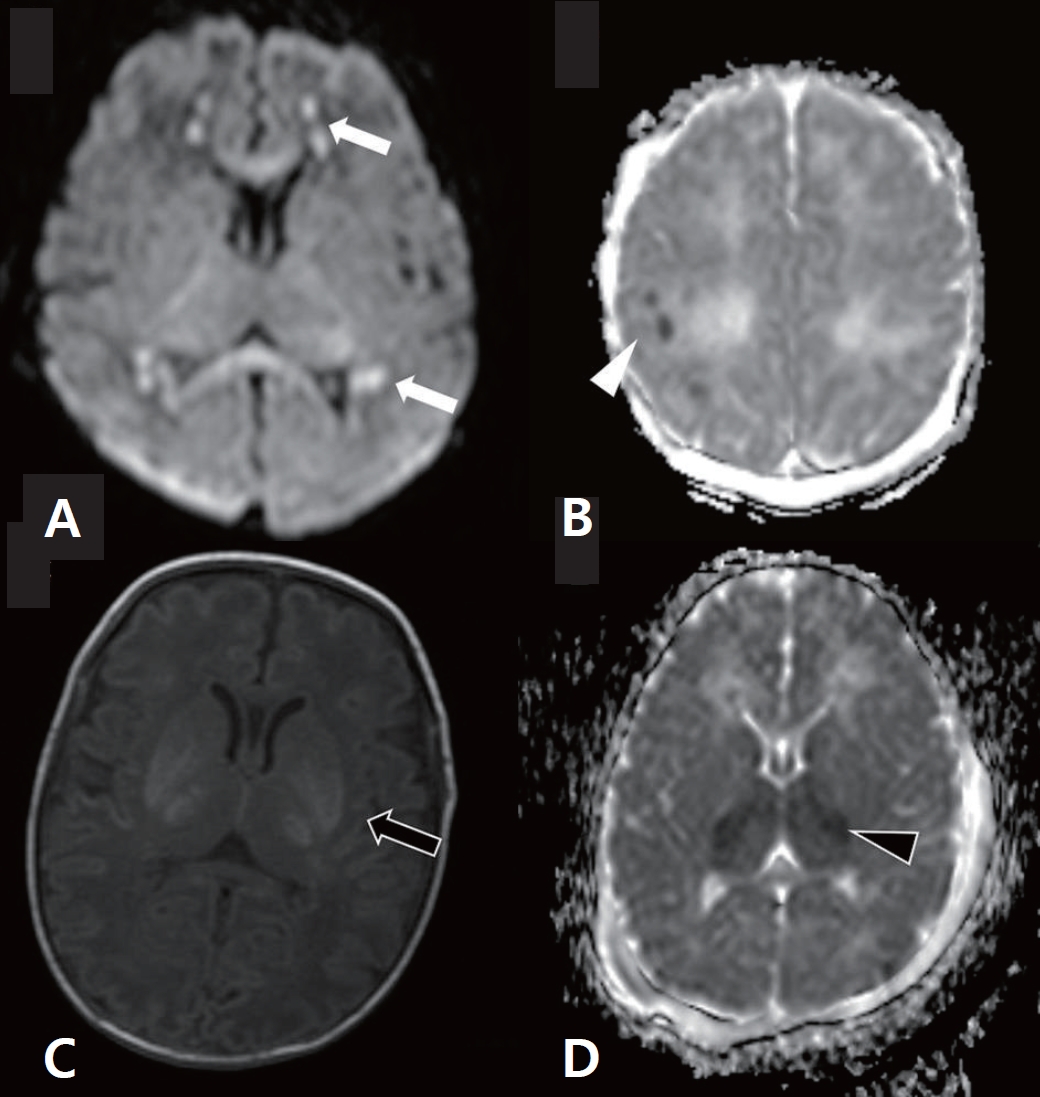
∙ Cognitive impairments occur in children with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) even without neuromotor deficits.
∙ Therapeutic hypothermia has improved neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with HIE; however, 40% of children remain at risk of death/disability or cognitive impairments necessitating the development of adjunctive neuroprotective therapies.
∙ Long-term follow-up until adolescence is required to identify cognitive dysfunction.
∙ A pattern of watershed injury on brain imaging is associated with poor cognitive outcomes.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of the role of ischemia modified albumin in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Mohamed A. Talat, Rabab M. Saleh, Mohammed M. Shehab, Naglaa A. Khalifa, Maha Mahmoud Hamed Sakr, Walaa M. Elmesalamy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):329-334. Published online August 15, 2020
-
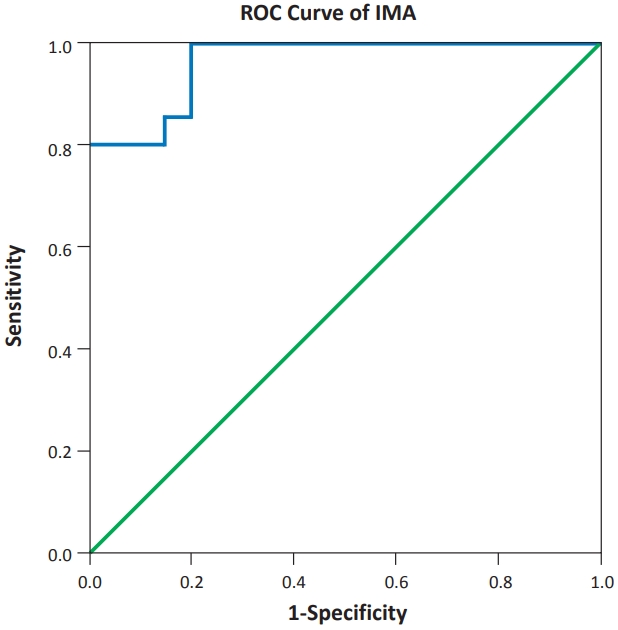
Question: What is the value of ischemia modified albumin (IMA) as a diagnostic marker for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Finding: IMA levels were significantly higher (nearly double elevation) in hypoxic than healthy newborns in the first few hours after birth in the full-term neonates.
Meaning: IMA can be a reliable marker for the early diagnosis of neonatal HIE and can be a predictor of injury severity.
- Hypoxia-inducible factor: role in cell survival in superoxide dismutase overexpressing mice after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia
- Ga Won Jeon, R. Ann Sheldon, Donna M Ferriero
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):444-449. Published online October 18, 2019
-
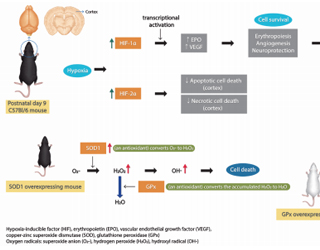
Background: Sixty percent of infants with severe neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy die, while most survivors have permanent disabilities. Treatment for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is limited to therapeutic hypothermia, but it does not offer complete protection. Here, we investigated whether hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) promotes cell survival and suggested neuroprotective strategies.
Purpose: HIF-1α-deficient mice have increased brain injury after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia (HI), and the...
- Case Report
- Gastroenterology
- Intestinal duplication revealed by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
- Yosra Kerkeni, Hela Louati, Mourad Hamzaoui
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(4):132-134. Published online April 23, 2018
-
We report a unique case of intestinal duplication detected on posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in a 13-year-old girl. She was admitted to the pediatric Emergency Department because of generalized seizures. Radiological assessment revealed a large, well-defined, thick-walled cystic lesion in the mid abdomen, suggestive of duplication cyst associated to a PRES. Exploration confirmed the diagnosis of ileal duplication cyst,...
- Neurology
- Mild encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion in a girl with acute pyelonephritis
- Jung Sook Yeom, Chung Mo Koo, Ji Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Eun Sil Park, Jae-Young Lim, Hyang-Ok Woo, Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):64-67. Published online February 28, 2018
-
We report the case of a 12-year-old girl who had mild encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS) associated with acutepyelonephritis caused by
Escherichia coli . The patient was admitted with a high fever, and she was diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis based on pyuria and the results of urine culture, which detected cefotaxime-sensitiveE. coli . Although intravenous cefotaxime and tobramycin were...
- Genetics and Metabolism
- The First Korean case of combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency-17 diagnosed by clinical and molecular investigation
- Young A Kim, Yoo-Mi Kim, Yun-Jin Lee, Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(12):408-412. Published online December 22, 2017
-
Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency-17 (COXPD-17) is very rare and is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in the
ELAC2 gene on chromosome 17p12. TheELAC2 gene functions as a mitochondrial tRNA processing gene, and only 4 different pathogenic mutations have been reported inELAC2 -associated mitochondrial dysfunction involving oxidative phosphorylation. Affected patients show various clinical symptoms and prognosis, depending on...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Clinical characteristics of hypertensive encephalopathy in pediatric patients
- Chang Hoon Ahn, Seung-A Han, Young Hwa Kong, Sun Jun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):266-271. Published online August 14, 2017
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to assess the clinical characteristics of hypertensive encephalopathy according to the underlying etiologies in children.
Methods We retrospectively evaluated 33 pediatric patients who were diagnosed as having hypertensive encephalopathy in Chonbuk National University Children's Hospital. Among the patients, 18 were excluded because of incomplete data or because brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was not performed. Finally,...
- Case Report
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome caused by presumed Takayasu arteritis
- Ki Wuk Lee, Sang Taek Lee, Heeyeon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S145-S148. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Takayasu arteritis (TA) is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that affects mainly the aorta, main aortic branches, and pulmonary arteries. Diverse neurological manifestations of TA have rarely been reported in children. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a neuroradiological condition that presents with headache, seizure, visual disturbances, and characteristic lesions on imaging. Inflammatory condition and severe hypertension in...
- Review Article
- Early-onset epileptic encephalopathies and the diagnostic approach to underlying causes
- Su-Kyeong Hwang, Soonhak Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):407-414. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Early-onset epileptic encephalopathies are one of the most severe early onset epilepsies that can lead to progressive psychomotor impairment. These syndromes result from identifiable primary causes, such as structural, neurodegenerative, metabolic, or genetic defects, and an increasing number of novel genetic causes continue to be uncovered. A typical diagnostic approach includes documentation of anamnesis, determination of seizure semiology, electroencephalography, and...
- Case Report
- Wernicke's encephalopathy in a child with high dose thiamine therapy
- So Won Park, Yoon Young Yi, Jung Woo Han, Heung Dong Kim, Joon Soo Lee, Hoon-Chul Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(11):496-499. Published online November 30, 2014
-
Wernicke's encephalopathy is an acute neurological disorder characterized by mental confusion, oculomotor dysfunction, and ataxia. It has been reported in individuals with alcohol dependence, hyperemesis gravidarum, and prolonged parenteral nutrition without vitamin supplementation. Here we present the case of a 13-year-old male patient with neuroblastoma and a history of poor oral intake and nausea for 3 months. After admission, he...
- Original Article
- Clinical outcome of acute necrotizing encephalopathy in related to involving the brain stem of single institution in Korea
- Cha Gon Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Munhyang Lee, Jeehun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(6):264-270. Published online June 30, 2014
-
Purpose Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE) is a fulminant disease of the brain characterized by bilateral thalamic lesions, and is prevalent among children in East Asia. The prognosis of ANE is usually poor with a high mortality rate and neurological sequelae. This study aimed to delineate the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of ANE.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed clinical data of 399 pediatric patients...
- Case Report
- X-linked recessive myotubular myopathy with
MTM1 mutations - Young-Mi Han, Kyoung-Ah Kwon, Yun-Jin Lee, Sang-Ook Nam, Kyung-Hee Park, Shin-Yun Byun, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(3):139-142. Published online March 18, 2013
-
X-linked recessive myotubular myopathy (XLMTM) is a severe congenital muscle disorder caused by mutations in the
MTM1 gene and characterized by severe hypotonia and generalized muscle weakness in affected males. It is generally a fatal disorder during the neonatal period and early infancy. The diagnosis is based on typical histopathological findings on muscle biopsy, combined with suggestive clinical features. We...
- A case of acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with parainfluenza virus infection
- Yoo-Na Kim, Su Jeong You
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(4):147-150. Published online April 30, 2012
-
Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE) may be suspected when a young child presents with abrupt onset of altered mental status, seizures, or both. Definitive clinical diagnosis is based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results. ANE is associated with influenza virus infections. Preliminary data suggests that up to 25% of ANE patients die, and up to 25% of ANE survivors develop substantial...
- A case of Hashimoto's encephalopathy presenting with seizures and psychosis
- Min-Joo Lee, Hae-Sang Lee, Jin-Soon Hwang, Da-Eun Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(3):111-113. Published online March 16, 2012
-
Hashimoto's encephalopathy (HE) is a rare, poorly understood, autoimmune disease characterized by symptoms of acute or subacute encephalopathy associated with increased anti-thyroid antibody levels. Here, we report a case of a 14-year-old girl with HE and briefly review the literature. The patient presented with acute mental changes and seizures, but no evidence of infectious encephalitis. In the acute stage, the...
- A case of tacrolimus-induced encephalopathy after kidney transplantation
- Myoung Uk Kim, Sae Yoon Kim, Su Min Son, Yong Hoon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(1):40-44. Published online January 31, 2011
-
We present a case of tacrolimus-induced encephalopathy after successful kidney transplantation. An 11-year-old girl presented with sudden onset of neurologic symptoms, hypertension, and psychiatric symptoms, with normal kidney function, after kidney transplantation. The symptoms improved after cessation of tacrolimus. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed acute infarction of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory in the right frontal lobe. Three days...
- A case of megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts
- Eun Young Park, Young Ok Kim, Ji Youn Kim, Chae Young Yeo, Hee Jo Baek, Chan Jong Kim, Eun Young Kim, Young Jong Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1342-1345. Published online December 15, 2008
-
Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts (MLC) is a rare white matter disorder, first described in the early 1990s. The brain in patients with MLC appears swollen on MRI, with diffuse white matter abnormalities; in addition, there is an invariable presence of subcortical cysts, primarily in the anterior temporal region sparing the deep white matter, basal ganglia, thalami, and cerebellum. Patients... -
- Original Article
- Clinical and Radiological Analysis of Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome in Children
- Hae-Ri Lim, Hye-Eun Seo, Sun-Hak Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):901-904. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome is a complex disorder with characteristic clinical and radiologic findings that mainly involve the white/gray matter of the parieto-occipital lobes. The purpose of this study was to determine its clinical and radiological characteristics. Methods : A total of 15 pateints were involved in the study. Their medical records and radiological features of brain MRI were... -
- Genotype of rotavirus isolated from patients with rotaviral enteritis and neurological complications
- Jae Hyung Choi, Jung Mi Kim, Yong Joo Kim, Jae Won Oh, Chang Lyul Kim, Myung Kul Yum, In Joon Sul, Jung Oak Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(5):513-518. Published online May 15, 2006
-
Purpose : This study was undertaken to determine the differences in genotypes of rotavirus and their incidence between patients with acute rotaviral enteritis who suffered neurologic complications and those who did not suffer neurologic complications. Methods : Among the 82 patients with rotaviral enteritis whose genotype was analyzed, 71 patients were not associated with neurologic complications(neurology(-) group), and eleven patients were... -
- CNS Complications in Childhood Cancer
- Yoo Jin Jeong, Yeon Kyong Seo, Seung Ah Hong, Heung Sik Kim, Jun Sik Kim, Hee Jung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(11):1112-1117. Published online November 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Recent advances in the methods of treating cancer in young patients have led to both an increased frequency of CNS complications as well as prolonged life expectancy. We intend to analyze the clinical aspects and laboratory findings of patients with CNS complications during and after treatment. Methods : We reviewed the medical records of 174 childhood cancer... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Nephritis Complicating Encephalopathy Accompanied by Hypertension and Cerebral Vasculitis
- Hee Ra Choi, Eo Jin Kim, Myoung Bum Choi, Jae Young Lim, Chan Hoo Park, Hyang Ok Woo, Hee Sang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(10):1040-1043. Published online October 15, 2003
-
Henoch-Shonlein purpura(HSP) is a systemic small-vessel vasculitis that primarily affects the skin, gastrointestinal tract, joints, and kidneys. The nervous system may be involved, less commonly than other organs. When the central nervous system(CNS) was involved, headache, changes in mental status, seizures, and focal neurologic deficits have been reported. Hypertension, uremic encephalopathy, metabolic abnomalities, electrolyte abnormalities, or cerebral vasculitis were suggested... -
- A Case of Influenza-associated Encephalopathy
- Yeoni Song, Chang Hwan Choi, Jong Woon Choi, Se Young Kim, Hyun Soo Kim, Yeol Kim, Dong Jin Im
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(10):1024-1028. Published online October 15, 2003
-
Influenza-associated encephalopathy is regarded as one of the major neurologic disease entities along with those of Reye syndrome, acute necrotizing encephalopathy, and myelitis which are known to be related to influenza virus, mostly type A. And it is being actively researched in Japan as it has caused a tremendous increase in the number of deaths from 1997 to 2002, but... -
- Original Article
- Leukoencephalopathy after CNS Prophylactic Therapy in Pediatric Hematologic Malignancy
- Jun Hwa Lee, Sun Min Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Kun Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(6):566-571. Published online June 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Leukoencephalopathy(LE) is one of the most serious complications in children with hematologic malignancies during the course of treatment. Early recognition is important to reduce the impact and sequelae from LE. We therefore investigated the clinical features of LE following central nervous system(CNS) prophylaxis in children with hematologic malignancies and evaluated the significance of regular check-ups of brain MRI. Methods... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Glutaric Aciduria Type I with Macrocephaly
- Woo Jong Shin, Yeo Ok Moon, Hye Ran Yoon, Eun Sil Dong, Young Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(3):295-301. Published online March 15, 2003
-
Glutaric aciduria type 1(GA1) is an autosomal recessive disorder of the lysine, hydroxylysine and tryptophan metabolism caused by the deficiency of mitochondrial glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase. This disease is characterized by macrocephaly at birth or shortly after birth and various neurologic symptoms. Between the first weeks and the 4-5th year of life, intercurrent illness such as viral infections, gastroenteritis, or even routine... -
- A Case of Incontinentia Pigmenti with Developmental Brain Malformation
- Suk Ho Kang, Soon Kim, Seung Hee Jung, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(4):535-539. Published online April 15, 2002
-
Incontinentia pigmenti is a rare neurocutaneous syndrome characterized by vesiculobullous skin disease in neonates and infants, a noninfectious disease that should be distinguished from infectious diseases with the neonatal seizure or encephalopathy. This disease is X-linked dominant with Xq28 region abnormalities and often associated with developmental defects of the ocular, skeletal, dental, and central nervous system. Central nervous system involvement... -
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy which Occurred During Chemotherapy in a Child with Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia
- Sang-Nam Bae, Bu-Jin Kim, Seong-Shik Park, Sang-Ook Nam, Young-Tak Lim, Hak-Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(11):1320-1325. Published online November 15, 2001
-
Wernicke,s encephalopathy(WE), a neurological disorder caused by thiamine deficiency, is characterized by the triad of ocular symptoms, ataxia, and mental confusion. More than 90% of the cases are observed in chronic alcoholics. Other conditions less frequently associated with WE are anorexia nervosa, prolonged parenteral nutrition, hemodialysis, uremia, hyperemesis gravidarum, gastroplasty for morbid obesity, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome(AIDS). One of the... -
- A Case of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy
- Sung Kee Kim, Se Wook Oh, Young Kyoun Kim, Se Chang Ham, Yong Won Park, Sang Woo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(8):954-958. Published online August 15, 2001
-
This disease predominantly affects infants and young children living in Japan and Taiwan, and manifests itself as acute encephalopathy following viral infections. The hallmark of this encephalopathy is multifocal, symmetric brain lesions affecting bilateral thalamus, brainstem tegmentum, cerebral periventricular white matter and cerebellar medulla, which can be visualized by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Both the gray and white... -
- A Case of Measles Encephalopathy with Thalamic Lesion on Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Dae Hun Pee, Dae Jin Song, Young Kyoo Shin, Jung Hwa Lee, Kee Hyoung Lee, Baik Lin Eun, Sang Hoon Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(8):936-941. Published online August 15, 2001
-
We experienced a case of measles encephalopathy with thalamic lesion on magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) in a 12 year old boy. Measles symptoms such as fever, erythematous maculopapular rashes on whole body and cough with sputum appeared 4 days before neurologic signs such as agitation and drowsy-to-confused mentality. He showed remarkable motor dysfunction without evidence of sensory loss. MRI showed bilateral... -
- Original Article
- Hemorrhagic Shock and Encephalopathy Syndrome as a Cause of Sudden Death in Infants
- Jong Won Lee, Chang Han Lee, Ki Sup Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(6):814-819. Published online June 15, 2000
-
Purpose : To evaluate the clinical characteristics, treatments and outcome of patients with hemorrhagic shock and encephalopathy(HSE) syndrome. Methods : We performed a clinical study on 14 patients who were diagnosed as hemorrhagic shock and having encephalopathy syndrome in the Department of Pediatrics, from 1984 to 1998. Age, sex, clinical symptoms and physical findings at admission, the most deranged laboratory findings,... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Fibromuscular Dysplasia Associated with Hypertensive Encephalopathy
- Ju Suk Lee, Sang Nam Bae, Sang Ook Nam, Su Young Kim, Hee Ju Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(5):715-719. Published online May 15, 2000
-
Fibromuscular dysplasia is the single leading etiology of renovascular hypertension in children. We report an eight-year-old girl who was admitted for generalized tonic seizure with fibromuscular dysplasia of right renal artery. On admission, she presented hypertension and altered mentality. She had suffered from intermittent severe headache for the past year. Renal angiography of right renal artery showed stenosis, beaded pattern... -
- Two Cases of Acute Encephalopathy with Symmetrical Low Density Areas in Bilateral Thalami in Siblings
- Soon Young Lee, Woo Jin Lee, Ji Eun Lee, So Yeon Kim, Jong Ho Lee, Seung Jae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(5):701-706. Published online May 15, 1998
-
-
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







