Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-

Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Not breastfeeding and risk of autism spectrum disorders among children: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):28-31. Published online July 19, 2022
-
This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between not breastfeeding (versus breastfeeding) and the risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) among children. We found that the risk of ASD associated with not breastfeeding had an odds ratio of 1.81 (95% confidence interval, 1.35–2.27; I2=0 %). These findings suggest the importance of breastfeeding in decreasing the risk of ASD among children.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Breastfeeding and vitamin D
- Ju Sun Heo, Young Min Ahn, Ai-Rhan Ellen Kim, Son Moon Shin; for the Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):418-429. Published online December 14, 2021
-
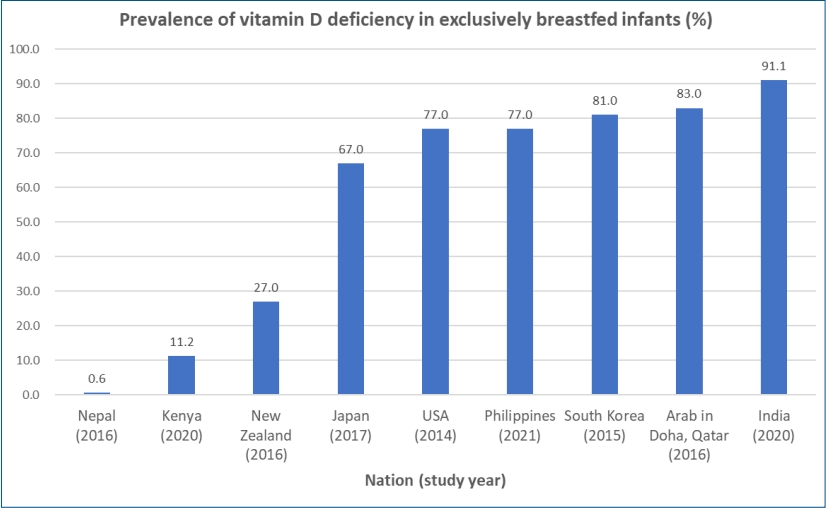
∙ Exclusively breastfed infants are at risk of developing vitamin D deficiency associated with hypocalcemia, rickets, and various health outcomes.
∙ The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants differs vastly between studies and nations at 0.6%–91.1%.
∙ The vitamin D content of breast milk does not meet the requirements of exclusively breastfed infants.
∙ Most international guidelines recommend that breastfed infants be supplemented with 400 IU/day of vitamin D during the first year of life.
∙ Vitamin D intake (milk+supplements) of 800 IU/day can be considered in preterm infants along with biochemical monitoring.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Early initiation of breastfeeding and factors associated with its delay among mothers at discharge from a single hospital
- J. Jenifer Florence Mary, R. Sindhuri, A. Arul Kumaran, Amol R. Dongre
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):201-208. Published online October 18, 2021
-

Background: According to the National Family Health Survey– 4, in India, 78.9% of deliveries occur in institutions, although only 42.6% of new mothers initiate breastfeeding within 1 hour of delivery.
Purpose: To estimate the proportion of early initiation of breastfeeding (EIBF) among new mothers at discharge from a tertiary care hospital and identify the determinants of delayed initiation of breastfeeding among...
- Significance of the tethered maxillary frenulum: a questionnaire-based observational cohort study
- Sody A. Naimer, Ariel Israel, Aviezer Gabbay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(3):130-135. Published online September 7, 2020
-

Question: Does a tethered maxillary frenulum in the newborn result in breastfeeding difficulty or other oral symptomatology?
Finding: The analysis of subjects with a tethered maxillary frenulum surveyed beyond a mean 5-year follow-up did not reveal an increase in oral issues versus those of a random agematched control group.
Meaning: These data demonstrate no need to intervene upon the diagnosis of a tethered maxillary frenulum.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- A perspective on partially hydrolyzed protein infant formula in nonexclusively breastfed infants
- Yvan Vandenplas, Zakiudin Munasir, Badriul Hegar, Dewi Kumarawati, Ahmad Suryawan, Muzal Kadim, Julistio Tb Djais, Ray Wagiu Basrowi, Deni Krisnamurti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):149-154. Published online January 14, 2019
-

The World Health Organization recommends that infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first 6 months of life to provide optimal nutrition in this critical period of life. After this, infants should receive nutritionally adequate and safe complementary foods while breastfeeding continues for up to 2 years of age or beyond. For nonbreastfed infants, infant formula is an available option...
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Maternal food restrictions during breastfeeding
- Goun Jeong, Sung Won Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Sun Young Ko, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):70-76. Published online March 27, 2017
-
Purpose This study investigated self-food restriction during breastfeeding, reviewed the literature showing the effect of maternal diet on the health of breast-fed infants, and explored the validity of dietary restrictions.
Methods Questionnaire data were collected from breastfeeding Korean mothers who visited the pediatric clinic of Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center from July 2015 through August 2015. The survey included items assessing...
- Vitamin D deficiency in infants aged 1 to 6 months
- You Jin Choi, Moon Kyu Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(5):205-210. Published online May 28, 2013
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to recognize the state of vitamin D among healthy infants aged 1 to 6 months in South Korea, and also to identify the risk factors affecting the level of vitamin D.
Methods A total of 117 infants were enrolled in this study for 12 months, from March 1, 2011 to February 29, 2012. Serum levels of...
- Review Article
- Nutritional management of breastfeeding infants for the prevention of common nutrient deficiencies and excesses
- Jin Soo Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(7):282-286. Published online July 31, 2011
-
Breastfeeding is the best source of nutrition for every infant, and exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months is usually optimal in the common clinical situation. However, inappropriate complementary feeding could lead to a nutrient-deficient status, such as iron deficiency anemia, vitamin D deficiency, and growth faltering. The recent epidemic outbreak of obesity in Korean children emphasizes the need for us to...
- Original Article
- A report on operating a nationwide human milk bank in Korea
- Kang Hoon Song, Yoo Min Lee, Ji Young Chang, Eun Young Park, Sung Ae Park, Nam Kyu Cho, Chong-Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):488-494. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Purpose : A human milk bank collects, processes, eliminates, and stores breast milk from donors and provides breast milk to those in need. The authors hereby present the experiences and the objective lessons obtained through operating a nationwide human milk bank over a period of 2 years. Methods : The characteristics of the donors and the recipients and the amounts of breast milk... -
- Incidence of breast milk jaundice in healthy full-term infants
- Yong Ho Yoon, Kyong Eun Choi, Kyung Ah Kim, Sun Young Ko, Yeon Kyung Lee, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(11):1072-1077. Published online November 15, 2007
-
Purpose : It has been described that the incidence of breastfeeding jaundice is 13% and that of breast milk jaundice is 2%. The incidence in Korea was believed to be higher, but there were no studies to prove this assumption. The purpose of this study was to investigate the incidence of jaundice of healthy breastfed full-term infants in Korea. Methods :... -
- Relactation in the Lactation Clinic
- Su Jin Cho, Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1050-1054. Published online October 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Relactation refers to the re-establishment of a milk supply and nursing after the cessation of nursing for a variable period. We aimed to analyze the practical issues related to successful relactation in the lactation clinic. Methods : The medical records of 51 mothers who had visited the lactation clinic for relactation were retrospectively analyzed. Breastfeeding greater than 90%... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Hypernatremic Dehydration in an Exclusively Breast-Fed Newborn Infant
- Kyung Pil Park, Jin Kyung Kim, Heng Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(6):790-795. Published online June 15, 2002
-
Sporadic reports of hypernatremic dehydration in breastfed newborn infants have appeared in medical literature for at least 3 decades. We report the first case of hypernatremic dehydration resulting from inadequate breast-feeding in Korea. A 14-day old baby, born to a mentally retarded mother, was transferred to our hospital with a body weight loss of 460 g since birth(17%) and a... -
- Original Article
- A Survey on Mothers' Perception of Breastfeeding
- Ji Hye Jung, Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(8):1050-1055. Published online August 15, 1999
-
Purpose : The objective of this investigation was to identify the postpartum change in breastfeeding rate and mothers' perception of breastfeeding. The investigation was carried out to make plans for the education of mothers regarding breastfeeding. Methods : Total of 284 mothers, who delivered healthy full-term babies at Dongdaemun Hospital, Medical College, Ewha Womans University, were interviewed and asked to complete... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







