Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Infection
- Febrile urinary tract infection in children: changes in epidemiology, etiology, and antibiotic resistance patterns over a decade
- Woosuck Suh, Bi Na Kim, Hyun Mi Kang, Eun Ae Yang, Jung-Woo Rhim, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):293-300. Published online October 14, 2020
-
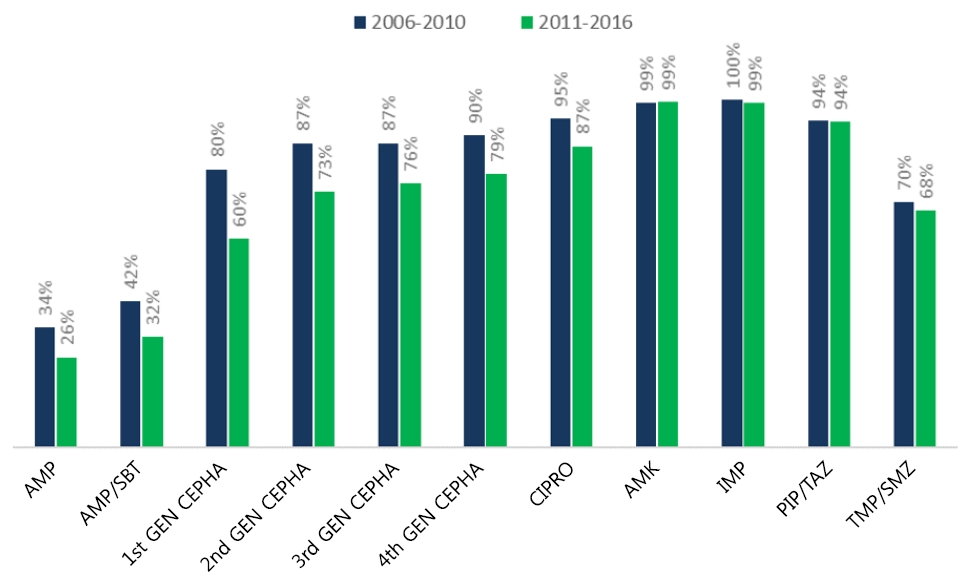
Question: How has the antibiotic susceptibility of urinary pathogens changed and what does it imply?
Finding: A yearly increase in multidrug-resistant and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)–producing pathogens was observed. A higher recurrence rate was observed in cases of febrile urinary tract infection caused by ESBL producers in patients with underlying vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
Meaning: The initial empirical antibiotic should reflect the changing susceptibility patterns and underlying VUR status.
- Case Report
- Liver abscess due to
Klebsiella pneumoniae in a healthy 12-year-old boy - Da Hye Yoon, Yeon Jin Jeon, E Young Bae, Dae Chul Jeong, Jin Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(11):496-499. Published online November 27, 2013
-
Pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) is rare in healthy children. We report a case of PLA in an immunocompetent 12-year-old boy. Percutaneous catheter drainage was performed for the abscess. In addition, parenteral antibiotics were administered for 3 weeks.
Klebsiella pneumoniae was detected in the culture of blood and drained fluid. Here, we present this case and a brief review of the...
- A case of pyogenic liver abscess in a 10-year-old girl
- Jung Lim Byun, Sun Hwan Bae, Sang Woo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(5):666-668. Published online May 31, 2010
-
Pyogenic liver abscesses are rare in children. In pediatric patients, altered host defences seem to play an important role. However, pyogenic liver abscess also occurs in healthy children. We experienced a case of pyogenic liver abscess in a healthy immunocompetent 10-year-old-girl. The patient presented two distinct abscesses: one subphrenic and the other intrahepatic. The intrahepatic abscess resolved with percutaneous drainage...
- Review Article
- Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia in children
- Hye-yung Yum
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):283-288. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Pneumonia remains the leading cause of mortality in children. Diagnosis depends on a combination of factors, including clinical assessment, radiological and laboratory findings. Although Streptococcus pneumoniae remains the most important cause of childhood bacterial pneumonia, the great majority of cases of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) are of viral etiology. A new, rapid, and inexpensive test that differentiates viral from bacterial pneumonia... -
- Original Article
- Bacteremia in pediatric cancer patients : A single center study
- Sun Mi Park, Byung Kyu Choe, Chun Soo Kim, Joon Sik Kim, Heung Sik Kim, Nam-Hee Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(8):882-888. Published online August 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Bacteremia is one of the major concerns in the treatment of pediatric cancer patients. This study was to determine the etiologic agents and the pattern of antibiotic susceptibilities in a single tertiary medical center. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of the cases of bacteremia in pediatric cancer patients from 1998 to 2005 in Keimyung University Dongsan... -
- Susceptibility tests of oral antibiotics including cefixime against Escherichia coli, isolated from pediatric patients withcommunity acquired urinary tract infections
- Soo Young Lee, Jung Hyun Lee, Jong Hyun Kim, Jae Kyun Hur, Sun Mi Kim, Sang Hyuk Ma, Jin Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(7):777-783. Published online July 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Urinary tract infection(UTI) is one of the most frequent infections in children. E. coli is the most frequent etiological micropathogen in pediatric community UTI, and E. coli has developed resistance to many antibiotics, highlighting the need for regular surveys of this organism resistant patterns in the community. The aim of this study was to determine the oral antibiotic... -
- Analysis of causative microorganisms and choice of antibiotics according to the onset of neonatal sepsis
- June Seung Sung, Dong Yeon Kim, Sun Hee Kim, Hyung Suk Byun, Tai Ju Hwang, Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):623-629. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The mortality rate of neonatal sepsis has been decreased, however, the incidence has not significantly decreased because of increased invasive procedures. This study was designed to make guidelines for choosing antibiotics by analyzing the causative microorganisms and their antibiotics sensitivity test according to the onset of neonatal sepsis. Methods : One hundred seven cases of culture proven sepsis... -
- A Clinical Study of Infective Endocarditis in Childhood
- Eun Na Choi, Jae Hun Kwon, Kyong Min Choi, Hwan Dae Hwang, Kyoung Mi Sin, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Dong Su Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(8):844-850. Published online August 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Advances in the treatment of congenital heart disease and a decline in the incidence of rheumatic fever has led to changes in the causative organisms and the clinical outcome of infective endocarditis(IE). We sought to analyze the clinical outcome, prognostic factors, causative organisms and corresponding antibiotic sensitivity in IE. Methods : Retrospective analysis of medical records of 104 children... -
- A Nationwide Survey on the Causative Organisms of Neonatal Sepsis in Korea
- Kyung Ah Kim, Son Moon Shin, Jung Hwan Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(1):55-63. Published online January 15, 2002
-
Purpose : A nationwide survey was conducted to investigate the most common causative organisms in neonatal sepsis in Korea. Methods : By reviewing medical records of newborn infants who were confirmed as neonatal sepsis by isolating organisms from blood culture during a one year study period from January to December in 1997, data for causative organisms, risk factors, accompanying focal infections and combinations of antibiotics... -
- The Relation between Antibiotic Use and Changes of Antimicrobial Resistance of Gram Negative Bacilli Isolated in Chonbuk National University Hospital(1993-1997)
- Min Ki Chang, Jung Min Chu, Hae Soo Lee, Jung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(5):625-631. Published online May 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Antimicrobial resistance has become a major medical and public health problem. This study was performed to evaluate the changes in antimicrobial susceptibility patterns. Methods : The susceptibility of 8,224 recent clinical isolates during a 5-year period from 1993 to 1997 were tested against 8 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrobial susceptibility test was performed by disc diffusion method. Results : E. coli... -
- A Study of Factors Affecting Time of First Stool in Premature Infants
- Hyeong Doo Cho, Je Woo Kim, Young Ah Lee, Hae Sun Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(12):1645-1650. Published online December 15, 1999
-
Purpose : To assess the effect of gestational age and illness severity, and the effect of antenatal exposure to magnesium sulfate, glucocorticoids, and antibiotics, on the timing of the first stool in preterm infants. Methods : Medical records of all preterm infants admitted to the neonatal ward at Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital between March 1998 and August 1998 were reviewed. We... -
- The Effect of Empirical Antibiotics in Febrile Neutropenia
- Ju Suk Lee, Young Tak Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(9):1209-1215. Published online September 15, 1998
-
Purpose : This study was designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of early cessation of antibiotic treatment regardless of absolute neutrophil count in children with febrile neutropenia and no identifiable infectious source. Methods : A prospective randomized clinical trial was performed in 93 episodes of fever in 37 neutropenic children with cancer, who were admitted to the Department of... -
- The Retrospective Study on Antibiotics Treatment in Acute Gastroenteritis
- Ji Hye Kim, Sung Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):826-834. Published online June 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Most of the gastroenteritis due to viruses and some bacteria can be successfully managed by oral and/or intravenous fluid-electrolyte replacement and antibiotic therapy is unnecessary and even harmful. It is, however, not uncommon practice to prescribe antibiotics when acute gastroentritis is suspected. Therefore authors analysed the clinical courses of the patients treated for acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis in a university hospital to assess... -
- A Study on Clinical Characteristics of Maxillary Sinusitis in Korean Children
- Dong Nam Kim, Sung Hee Oh, Hahng Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(3):319-327. Published online March 15, 1995
-
Purpose : Paranasal sinusitis, easily overlooked owing to it's benign symptomatology, should be considered when the upper respiratory tract infction persists longer than seven days. Without early recognition and appropriate management, the disease will take a chronic course and the incidence of complications will be increased. The significance of paranasal sinusitis among Korean children has not appropriately been appreciated; therefore,... -
- Prevalence Rate of Shigella Subgroup Infection & Changing Pattern of Their Antibiotics Susceptibility During Last Twenty Years.
- Kyung Sin Kim, Myung Sung Moon, Keun Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(5):455-462. Published online May 31, 1983
-
Among bacterial enteritis of hospitalized Korean children, shigellosis was the most frequent diarrheal disease. During the ten-year period(1972〜 1981), 319 strains of shigella were isolated from 319 different diarrheal patients; 261 of 319 strains(81.8%) were Shigella flexneri, 49(15.3%) were S.sonnei, 5 and 4(1.5% & 1.2%) were S. boydii and S. dysenteriae, respectively. Every year S. flexneri appeared to be the most frequent... -
- Clinical and Bacteriological Studies of Urinary Tract Infection in Children.
- Jin Yeong Jeong, Ho Jin Lee, Don Hee Ahn, Keun Chan Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(1):45-55. Published online January 31, 1981
-
Clinical and bacteriologicaql studies on 133 cases of urinary tract infection who were admitted to the Dept. of Pediatrics, NMC during the period of Jan. 1974 to Jan. 1979 were subjected in this study. The resultes were as follows : 1. Among the total 133 cases, 100 cases(75.2%) were male and 33 cases(24.8%) were female with sex ratio of 3:1.... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







