Most cited
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most cited
Most-cited articles are from the articles published during the last two years (2022 ~ ).
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- Gyu Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):384-394. Published online December 28, 2022
-
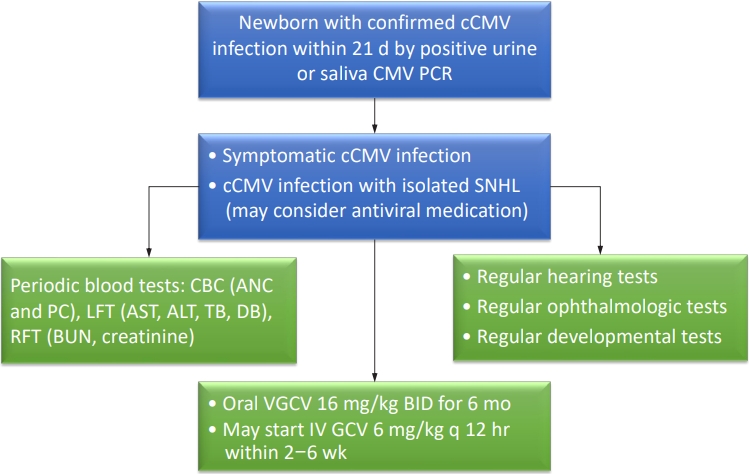
· Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is among the most common causes of nongenetic sensorineural hearing loss.
· Congenital CMV is initially treated with intravenous ganciclovir for 2–6 weeks and switched to oral valganciclovir, or with oral valganciclovir for the entire 6-month period.
· Infants with congenital CMV require periodic monitoring of absolute neutrophil count, platelet count, and blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver function tests, audiological, ophthalmological, and developmental tests during antiviral medication.
- Other
- Hearing loss in neonates and infants
- Goun Choe, Su-Kyoung Park, Bong Jik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):369-376. Published online January 9, 2023
-

· Congenital hearing loss is common, with an approximate incidence of 1.5 per 1,000 newborns and affecting 1.2%–11% of preterm and 1.6%–13.7% of neonatal intensive care unit neonates.
· Etiologies vary, and up to 80% of cases are genetic.
· Newborn hearing screenings follow the 1-3-6 rule, and babies at high risk of hearing loss should be referred to otolaryngology for early detection and timely intervention.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Ozlem Kara, Hanife Aysegul Arsoy, Murat Keskin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):395-402. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: Is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adolescents?
Finding: The frequency of NAFLD did not increase in adolescents with PCOS. However, hyperandrogenemia was a risk factor for NAFLD.
Meaning: Adolescents with PCOS and hyperandrogenemia should be closely monitored for hepatic steatosis.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
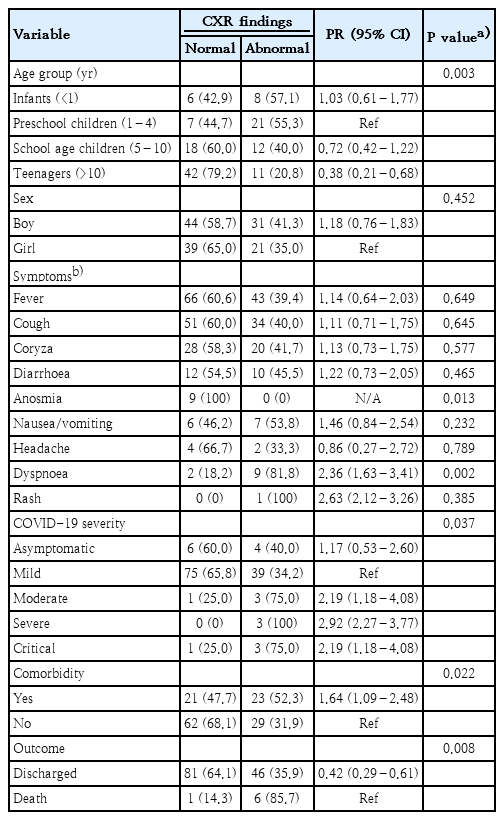
- Chest x-ray findings in children with COVID-19: lesson learned from referral hospitals in Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
- Andrew Limavady, Eka Airlangga, Ririe Fachrina Malisie, Ayodhia Pitaloka Pasaribu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):317-319. Published online May 16, 2023
-
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children
- Mauro Cinquetti, Vanessa Dargenio, Michele Fingerle, Carolina Marchiotto, Marco Biasin, Massimo Pettoello Mantovani, Flavia Indrio
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):226-232. Published online December 21, 2022
-
· Social media use can cause adverse health outcomes, including gastrointestinal disorders, in children and adolescents.
· Recent findings have shown a high prevalence of social media use and decreased well-being in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
· The biopsychosocial nature of functional gastrointestinal disorders and the clear influence of social media on the psychosocial lives of children suggests the likely involvement of social media in their development.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Parenting stress and interactive engagement behaviors in children with developmental delay
- Jung Sook Yeom, Rock Bum Kim, Jae Young Cho, Ji Sook Park, Eun Sil Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jae-Young Lim, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):252-261. Published online May 19, 2023
-
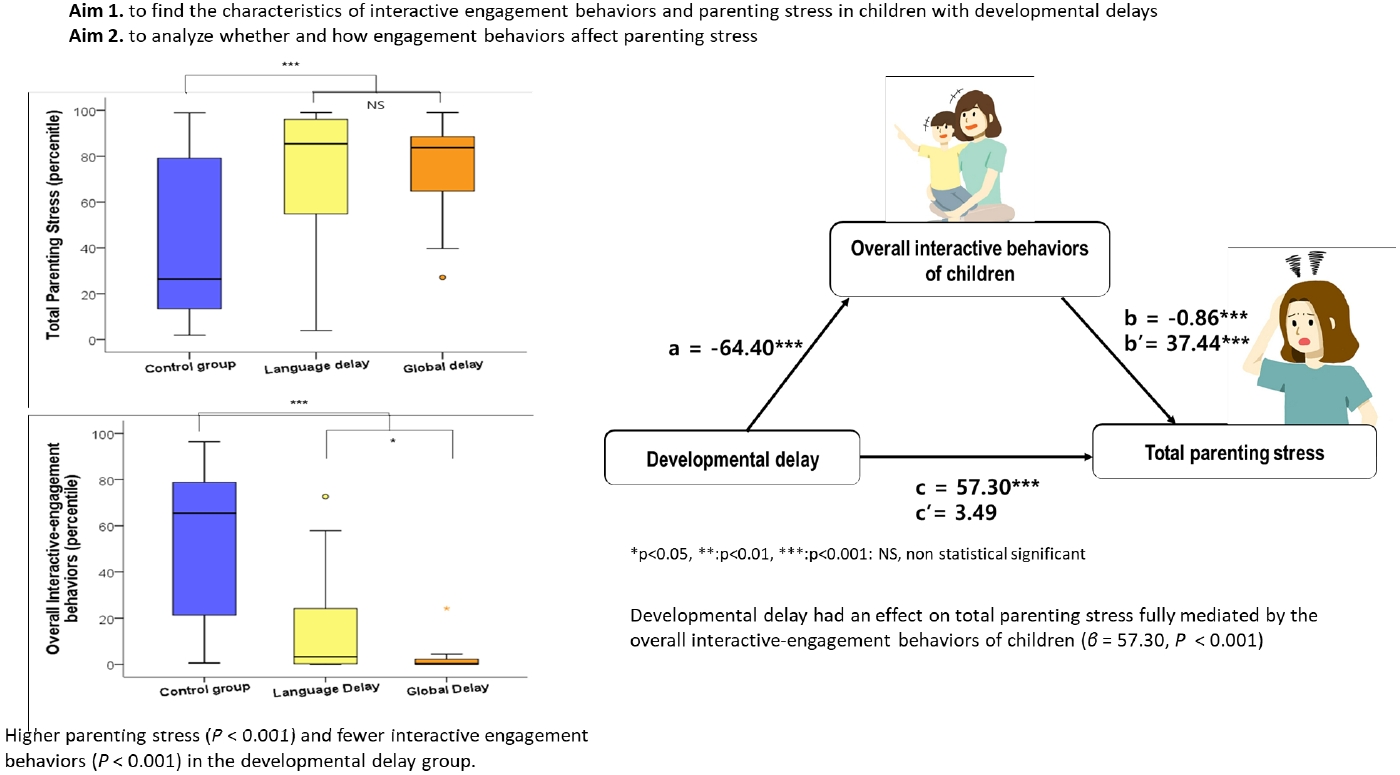
· Question: What level of parenting stress is experienced by parents of children with developmental delays (DDs) without autism spectrum disorder, and what factors contribute to it?
· Findings: Parents of children with DDs experienced high parenting stress that were significantly mediated by their children’s low interactive behaviors.
· Meaning: The interactive behaviors of children with DDs mediate parenting stress.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children
- Yogesh Waikar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):155-160. Published online October 17, 2022
-
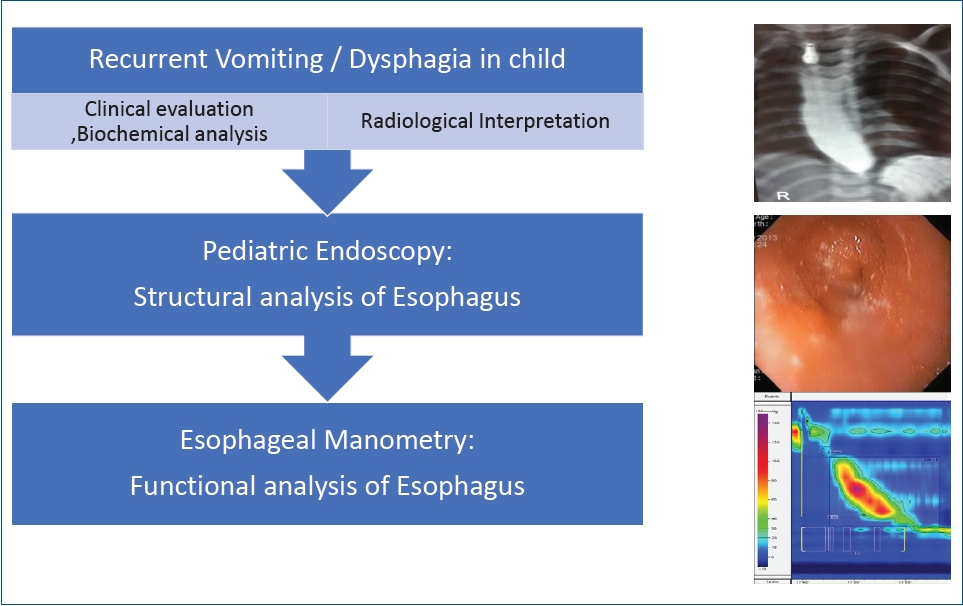
High-resolution esophageal manometry can be safely performed in children where recurrent vomiting and persistent dysphagia is the working diagnosis after excluding nonluminal and structural obstructive pathologies using pediatric upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Normal manometry values are available. Clinical picture, biochemical tests, radiological interpretation, and endoscopic findings with manometry completes the analysis of patients with recurrent vomiting and dysphagia.
- Allergy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy
- In Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):161-168. Published online October 25, 2022
-
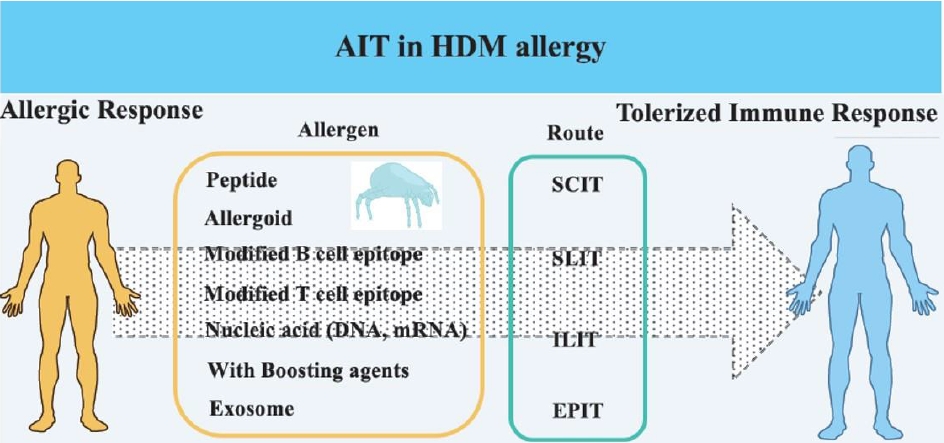
Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) has developed over the last few decades and has emerged as a promising treatment. House dust mite (HDM) is a target allergen in AIT, and various modified HDM allergens have been improved for their efficacy. Moreover, clinical trials have proved their significantly therapeutic effects in allergy. This article review focuses on HDM allergens developed for AIT efficacy,...
- Original Article
- Infection
- Predicting COVID-19 transmission in a student population in Seoul, South Korea, 2020–2021
- Young Hwa Lee, Han Ho Kim, Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(4):173-178. Published online December 22, 2022
-
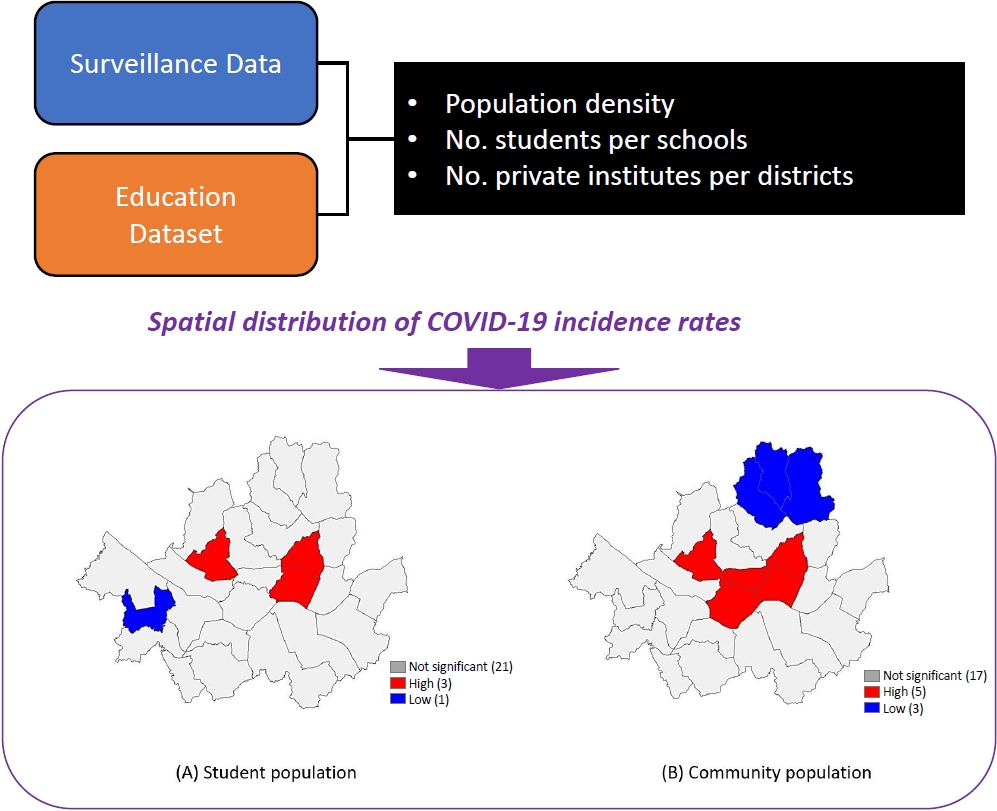
Question: What is the spatial distribution and determinants of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection among students in Korea?
Finding: The community population was closely associated with the risk of COVID-19, and the number of students per school class were inversely associated with COVID-19 rates in students.
Meaning: Our finding suggests that controlling the community-level burden of COVID-19 can help prevent sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in school-aged children.
- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Biallelic POLR3A variants cause Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch syndrome with atypical brain involvement
- Byungseung Moon, Minhye Kim, Hye Jin Kim, Jae So Cho, Hey Joon Son, Byung Chan Lim, Ki Joong Kim, Jong Hee Chae, Soo Yeon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):142-144. Published online December 30, 2022
-

- Letter to the Editor
- Endocrinology
- Accuracy of predicted adult height using the Greulich-Pyle method and artificial intelligence medical device
- Dongho Cho, Yun Sun Choi, Hayun Oh, Young min Ahn, Ji-Young Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):145-147. Published online January 25, 2023
-
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Pediatric syncope: pearls and pitfalls in history taking
- Jung Sook Yeom, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):88-97. Published online February 15, 2023
-
An accurate diagnosis depends on correct history taking and its interpretation. An in-depth understanding of the symptoms of syncope in connection with its pathophysiology can lead to avoiding critical pitfalls in the diagnostic process of history taking.
- Editorial
- Emergency Medicine
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children: teamwork approach
- Ji-Hyun Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):66-67. Published online September 1, 2022
-
· The successful and safe enema reduction of intussusception depends primarily on the experience and preference of the radiologists and the availability of resources.
· The establishment of a standardized manual or protocol for reduction and pre-reduction treatment of intussusception, along with the collaboration of pediatricians, radiologists, and surgeons, is expected to improve the treatment success rate.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Pathogenetic and etiologic considerations of febrile seizures
- Ji Yoon Han, Seung Beom Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):46-53. Published online January 13, 2023
-
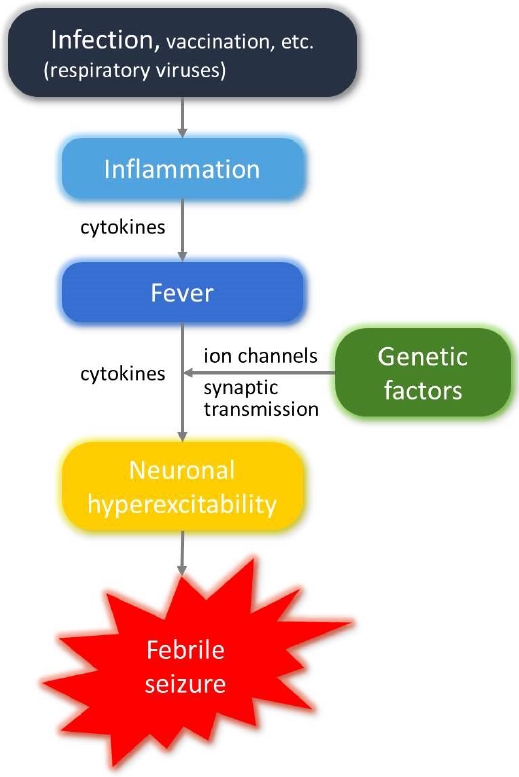
· Inflammatory responses accompanying fever increase neuronal excitability in the central nervous system, which in turn provokes seizures.
· Fever in children with febrile seizures is usually caused by common respiratory viruses, the distributions of which match those of seasonal community-acquired respiratory tract infections.
· Several genetic variations in ion channels seem associated with neuronal hyperexcitability in children with febrile seizures.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Virtual reality for pain reduction during intravenous injection in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Masoud Rafiee, Mozhdeh Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):533-537. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: This is the first meta-analysis to examine published evidence of the effectiveness of virtual reality at reducing pain during pediatric intravenous injections.
Finding: Our results suggest that virtual reality effectively reduces pain associated with intravenous injections in pediatric patients.
Meaning: These findings suggest the importance of virtual reality in decreasing the pain of intravenous injections among children.
- Gastroenterology
- Inferior vena cava to aorta ratio in dehydrated pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Gilbert Sterling Octavius, Michelle Imanuelly, Johan Wibowo, Nadia Khoirunnisa Heryadi, Melanie Widjaja
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):477-484. Published online June 14, 2023
-
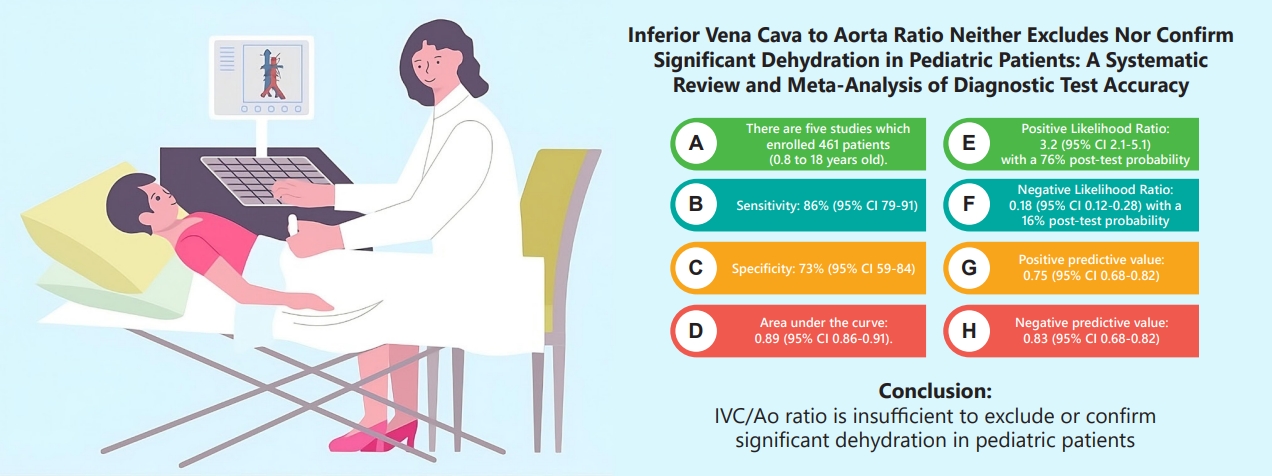
Question: The inferior vena cava to aorta (IVC/Ao) ratio measured via ultrasound has been touted as a promising noninvasive technique to assess clinically significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
Finding: Our meta-analysis found that IVC/Ao ratio had a positive likelihood ratio of 3.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–5.1) and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12–0.28).
Meaning: Hence, IVC/Ao ratio is insufficient to exclude or confirm significant dehydration in pediatric patients.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between maternal coronavirus disease 2019 and transient tachypnea of the newborn: a single-center study
- Sung Hee Lee, Ju Hyun Jin, Jong Ha Yoo, Shin Won Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(11):493-500. Published online October 24, 2023
-
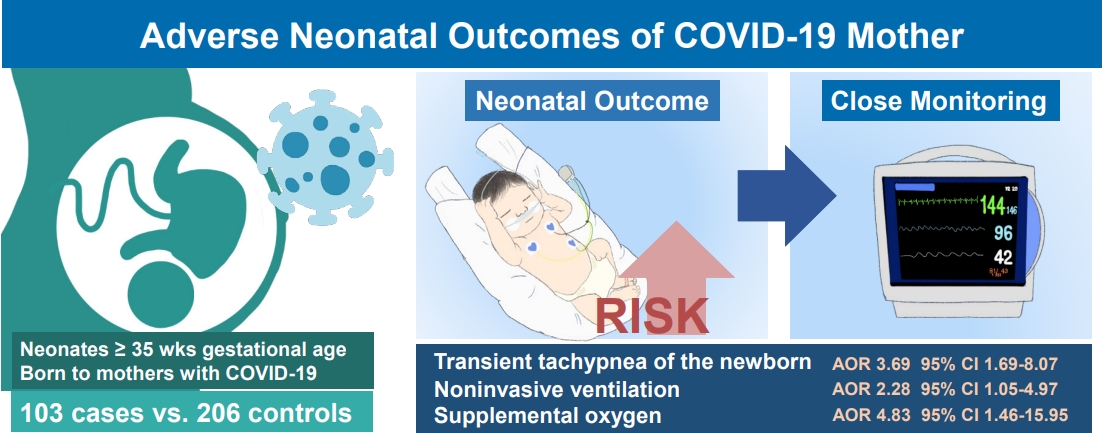
Question: What are the adverse clinical outcomes of neonates of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)–infected mothers?
Finding: Infants of mothers with COVID-19 were at significantly increased risk of transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), use of noninvasive ventilation, and need for supplemental oxygen (P<0.05).
Meaning: Neonates of mothers with COVID-19 are at risk of TTN and require respiratory support. Close monitoring is essential to ensuring timely intervention if required.
- Review Article
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders
- Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):432-438. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAID) are disorders caused by dysregulation of the innate immunity with genetic background, leading to recurrent episodes of systemic inflammation.
· SAID is characterized by recurrent acute inflammatory responses including fever or skin manifestations, unrelated with infection or malignancy.
· Diagnosis is based on family and long-term history with detailed clinical and laboratory manifestations during febrile periods.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Neonatal risk factors associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an umbrella review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Erfan Ayubi, Sajjad Farashi, Saeid Bashirian, Fereshteh Mehri
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):441-446. Published online July 14, 2023
-
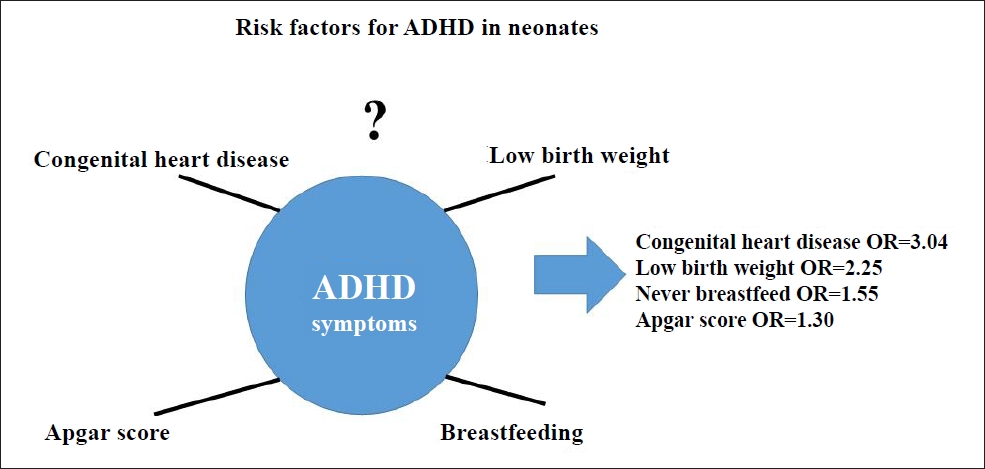
Question: The risk factors for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), such as breastfeeding, congenital heart disease, and low birth weight, in neonates are not well understood.
Finding: This umbrella review obtained significant effect sizes for ADHD for congenital heart disease (odds ratio [OR], 3.04), low birth weight (OR, 2.25), never breastfed (OR, 1.55), and Apgar score (OR, 1.30).
Meaning: Congenital heart disease, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, and Apgar scores were significant factors for ADHD.
- Editorial
- Immunology
- Systemic autoinflammatory disorders: autoinflammatory and autoimmune disorders
- Young Dae Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(10):439-440. Published online July 4, 2023
-
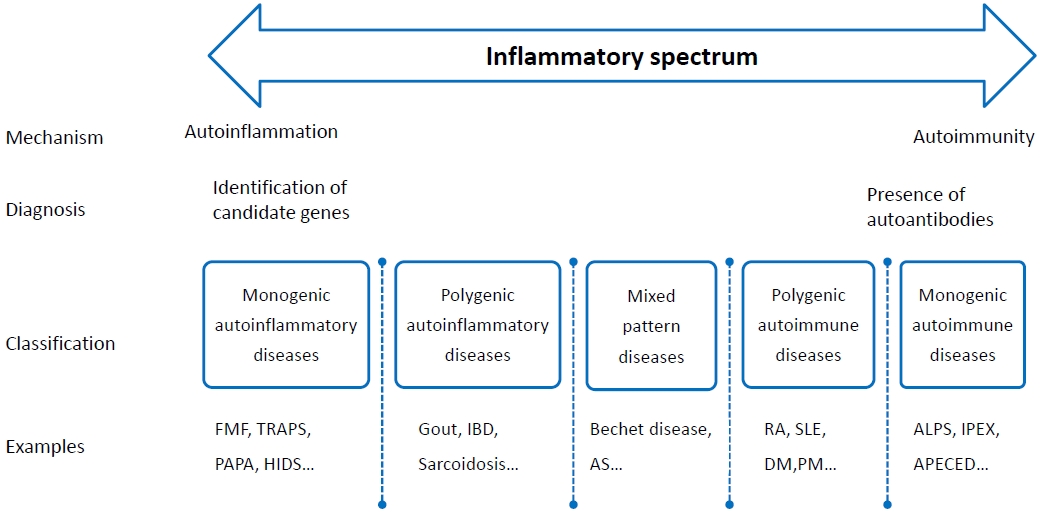
· Systemic autoinflammatory disorders (SAIDs) typically have an early onset in life, and may have close relatives may have similar disease.
· SAIDs should be suspected in any patient, especially children, who experience persistent or recurrent inflammatory episodes that fail to fit the pattern of other established diseases.
· Advancements in the understanding of autoinflammation will provide novel diagnostic and therapeutic options for SAIDs patients.
- Pulmonology
- Community-acquired pneumonia in Korean children: time to read between the lines
- Dong In Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):22-23. Published online November 10, 2022
-
· Various studies have reported the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in Korean children
· Factors other than etiology are equally important to a compre hensive understanding of CAP
· Knowledge from archived reports is no longer directly applicable to the current CAP and requires careful modification
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- A thickened formula reduces feeding-associated oxygen desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants
- Gayoung Lee, Juyoung Lee, Ga Won Jeon, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):32-37. Published online December 15, 2022
-
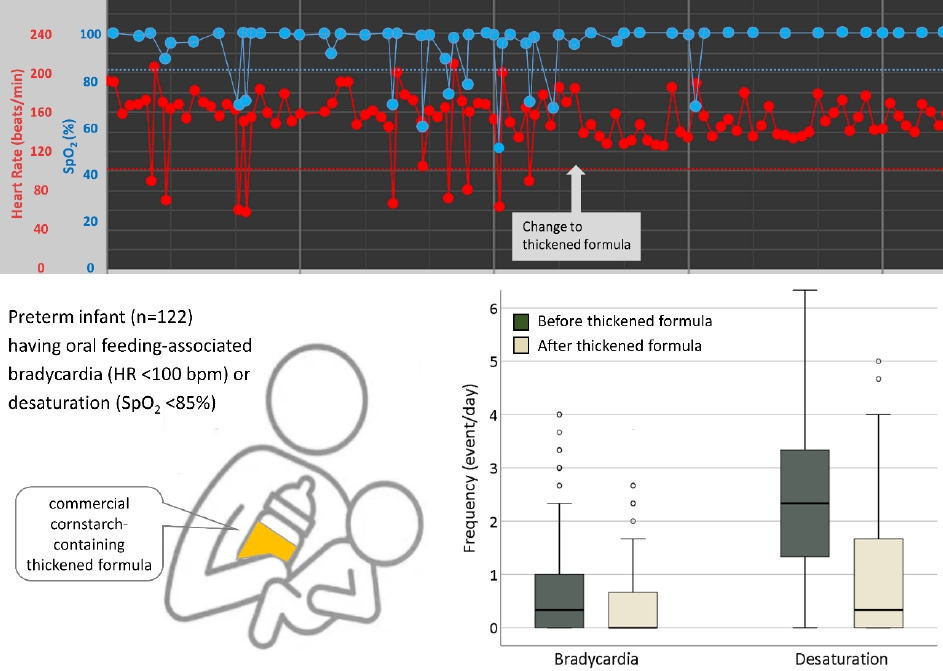
Question: Is a commercial thickened formula able to alleviate oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants?
Finding: Thickened formula feeding significantly reduced oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants.
Meaning: Thickened formula feeding stabilizes oxygen saturation and heart rate during oral feeding among preterm infants with feeding difficulties.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Characteristics of z score systems for diagnosing coronary abnormalities in Kawasaki disease
- Gyeong-Hee Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):448-449. Published online March 14, 2022
-
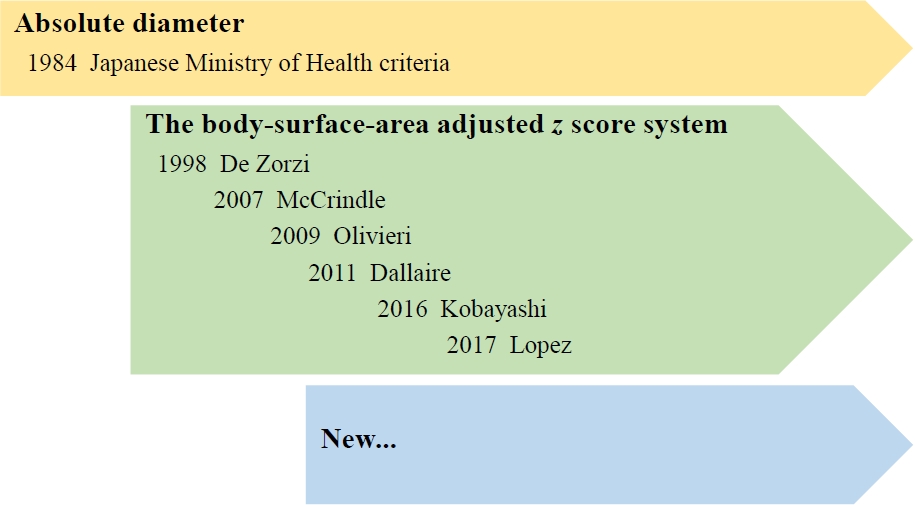
Because of the various body sizes of children with Kawasaki disease (KD), coronary artery diameter requires normalization to the body surface area as a z score.
In updated guidelines, coronary artery abnormalities are important criteria in the diagnosis of KD, and z score systems have been accepted to define coronary artery abnormalities.
However, the z score formula should be selected carefully because each yields different results.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Effect of cyclic pamidronate administration on osteoporosis in children with β-thalassemia major: a single-center study
- Mahmoud A. El-Hawy, Nagwan Y. Saleh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):405-409. Published online June 7, 2022
-
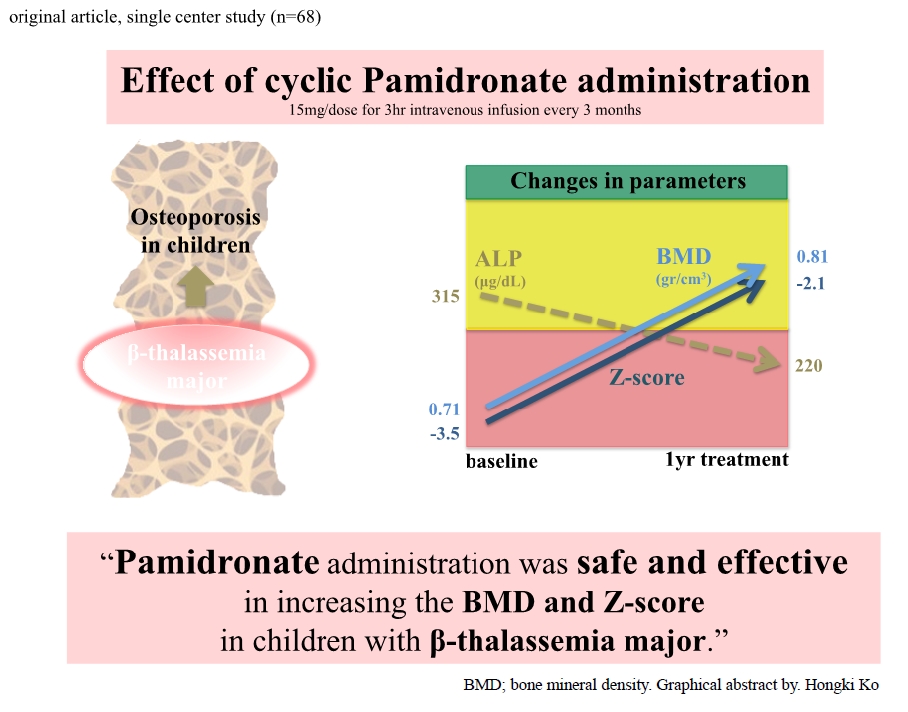
Question: What is the effect of cyclic pamidronate administration on osteoporosis in children with β-thalassemia major?
Finding: The dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan findings of children with β-thalassemia major and osteoporosis were improved after pamidronate administration.
Meaning: Cyclic pamidronate effectively treated osteoporosis in children with β-thalassemia major.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Coronavirus disease 2019 and mRNA vaccines: what’s next – miRNA?
- Joon Kee Lee, Heon-Seok Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):302-303. Published online March 28, 2022
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small single-stranded noncoding RNA molecules that function in RNA silencing and the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. The potential role of miRNAs as biomarkers of myocarditis is promising, and miRNAs are expected to be utilized in various clinical fields in the future.
- Endocrinology
- Is type 1 diabetes related to coronavirus disease 2019 in children?
- Minsun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):252-253. Published online March 29, 2022
-
· Evidence shows that patients with type 1 diabetes have been severely affected by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in various ways.
· Although there is no reliable evidence that COVID-19 worsens or induces diabetes, it can impair β-cell insulin secretion and glucose control by inducing inflammation and cytokine production.
· A study is needed of the short- and long-term relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 in the Korean pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Emergency Medicine
- Nonfatal injuries in Korean children and adolescents, 2007–2018
- Gyu Min Yeon, Yoo Rha Hong, Seom Gim Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):194-200. Published online September 9, 2021
-

Question: How many children and adolescents have experienced nonfatal injuries in the previous year?
Finding: Among Korean children and adolescents, 8.1% experienced at least one injury per year. We found no significant change in the incidence of injuries over the previous 12 years.
Meaning: The incidence of injuries is higher than this estimation; therefore, more attention and effort are needed to prevent injuries among children and adolescents.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Importance of maintaining a high childhood vaccination rate and surveillance program against Japanese encephalitis in Korea
- Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):127-128. Published online February 16, 2022
-
∙ Recent epidemiologic changes of Japanese encephalitis (JE) in Korea are area (rural to urban or suburban) and age shift (children to adult).
∙ Although the main factors contributing to recent epidemiologic changes of JE are not well identified, maintaining high vaccination rates of JE appear to be important in preventing of JE in all age groups.
∙ Continuous surveillance for epidemiology and seroprevalence should be carried out.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
- Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
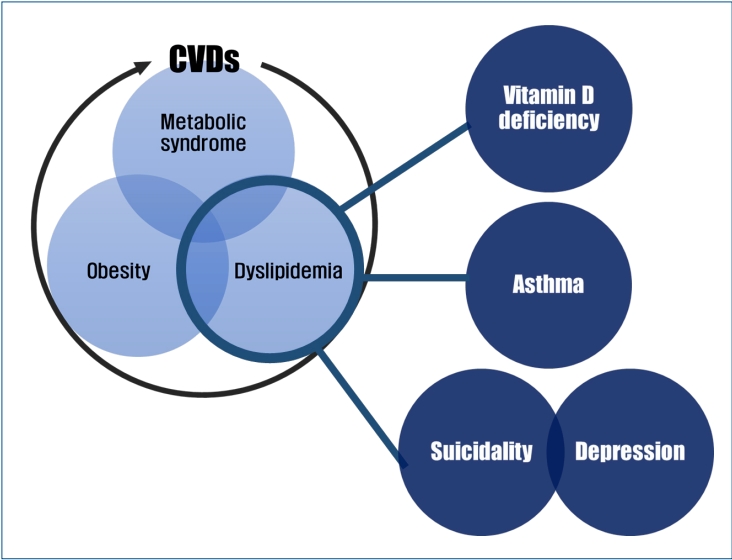
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in various pediatric neurologic diseases
- Jeongho Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):81-82. Published online January 6, 2022
-

Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has many important biomarkers that are commonly analyzed in pediatric neurologic diseases, including central nervous system infection and inflammation. Neurologic disease in pediatrics is difficult to diagnosis, there are challenges in developing CSF profiles. Some biomarkers are expected to help differential diagnosis.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by








